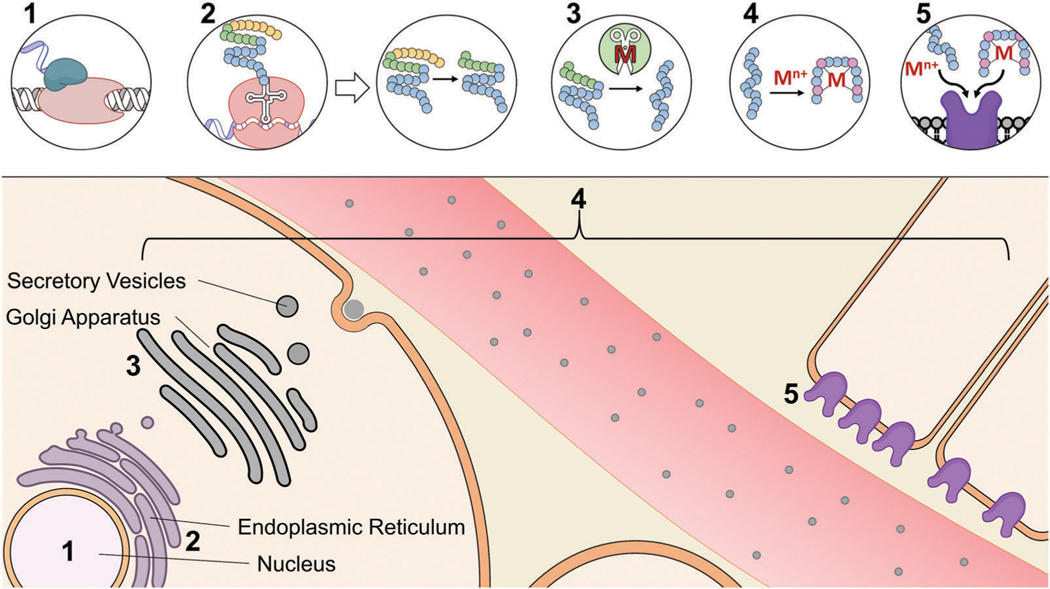
Fig. 2.
The central dogma of a metal binding peptide hormone: synthesis, maturation and action of protein and peptide hormones and proposed interactions of metals in this pathway. (1) First, the hormone associated gene is transcribed. (2) The preprohormone is translated in the ER and the signaling sequence (yellow) is cleaved yielding a prohormone. (3) The prohormone is further cleaved to arrive at the mature hormone (blue). (4) Metals can bind the hormone and impact structure, bioactivity, and circulation lifetime and stability. This interaction can occur throughout the maturation of a metal binding peptide from as early as translation to the binding of the peptide with its target. (5) Hormones bind their target receptor to initiate signaling cascades. Metal binding can change the conformation of a hormone to affect the affinity for its receptor or directly facilitate hormone–receptor complex formation.