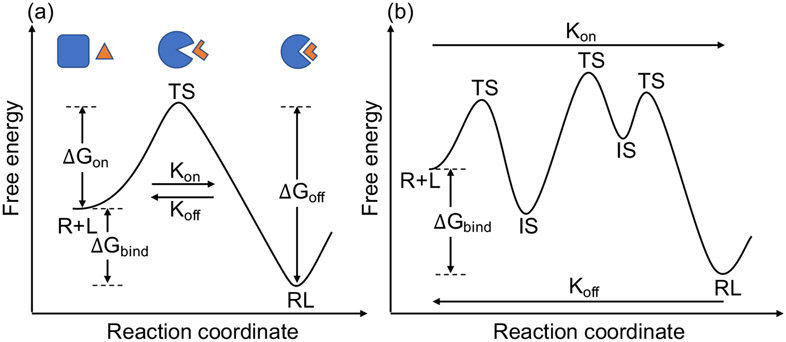
Figure 7:
A simplified representation of the binding kinetics between the unbound receptor (R), unbound ligand (L) and the bound receptor-ligand complex (RL). (a) The binding kinetics of a system with only one transient state (TS) along the binding reaction coordinate. The figure shows a binding scenario where both receptor and ligand undergo conformational changes in the binding process. The kinetic residence time (i.e., the inverse of the RNA-ligand dissociation constant koff) depends on the free energy difference (ΔGoff) between the bound state and transient state, while the thermodynamic binding energy (ΔGbind) is determined by the free energy difference between the unbound state (R+L) and bound state (RL). (b) In practice, often the binding kinetic profile of a system contains multiple transient states (TS) and intermediate states (IS) with a much more complicated kinetic mechanism.