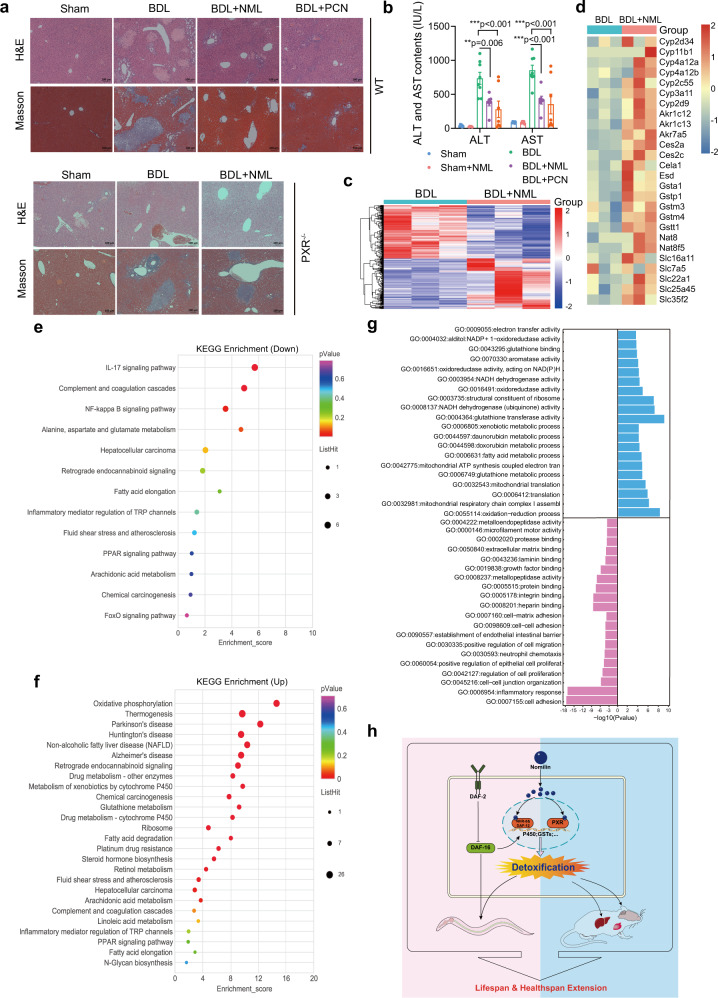
Fig. 10. Nomilin protects BDL-induced liver cholestatic injury through mPXR and upregulates longevity related genes in mice.
a Pictures showing H&E or Mason staining of liver sections in BDL mice with or without PCN and nomilin supplementation. Nomilin effectively attenuated the BDL-induced liver damage in WT (upper), but not in PXR-/- mice (bottom). b Bar-graphs showing the levels of serum ALT and AST in sham or BDL mice (n = 7 for BDL + NML and BDL + PCN, n = 8 for BDL). The data are shown as mean ± SEM. p-values were determined by one-way ANOVA test. ***p < 0.001 vs BDL group. c, d The RNA-seq hierarchical clustering heatmap showing differentially expressed genes (c) and genes in the detoxification process (d) from control (BDL) and nomilin-treated (BDL + NML) mouse liver under BDL surgery. e, f A chart showing the downregulated (e) and up-regulated (f) differentially expressed genes of KEGG pathways compared with the control group in both nomilin-treated and long lifespan mice. g A chart showing the top 20 up-regulated (blue) and downregulated (pink) molecular functions and biological processes (GO). h A diagram depicting the effects of nomilin on longevity through the activation of nuclear hormone receptors and detoxification signalling in C. elegans and mice.