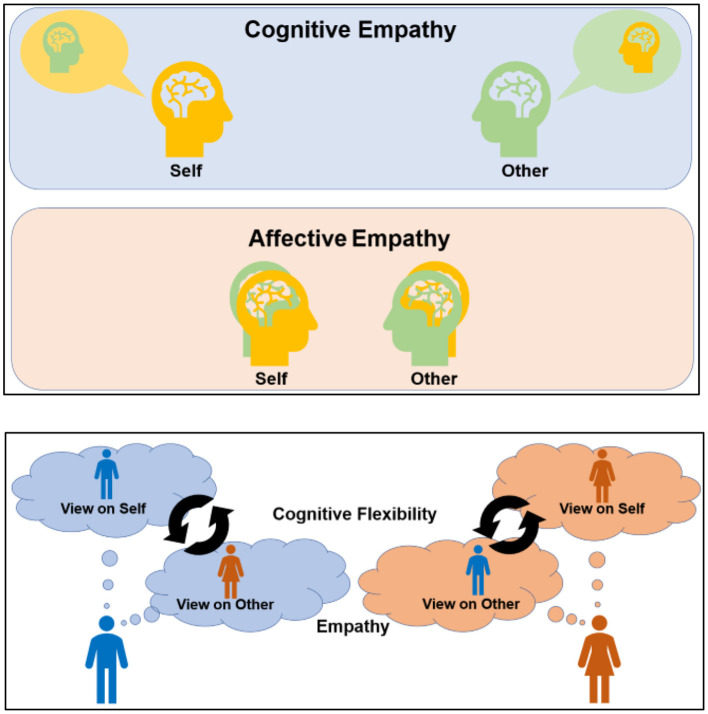
Figure 1.
Illustration of empathy and cognitive flexibility. CogEMP allows individuals to obtain accurate knowledge regarding the content of another person's mind and often requires a self–other distinction to identify others' minds more clearly. Meanwhile, AffEMP promotes the sharing of others' feelings, such as joy and distress and involves the self–other overlap of emotional experiences (upper panels). Cognitive flexibility requires self-control to adapt to changing environments via shifts in decision rules and perspectives. It also supports the switching and maintenance of perspectives between the self and others to facilitate empathy, which prompts social communication that is adaptable and context-adjusted (lower panel). Meanwhile, altered cognitive flexibility and empathy may hinder flexible emotion regulation and shifting attention and perspectives. They can maladaptively amplify shared distress and perspective bias (empathic inaccuracy), which can prompt people to acknowledge interpersonal communication or experiences as socially traumatic.