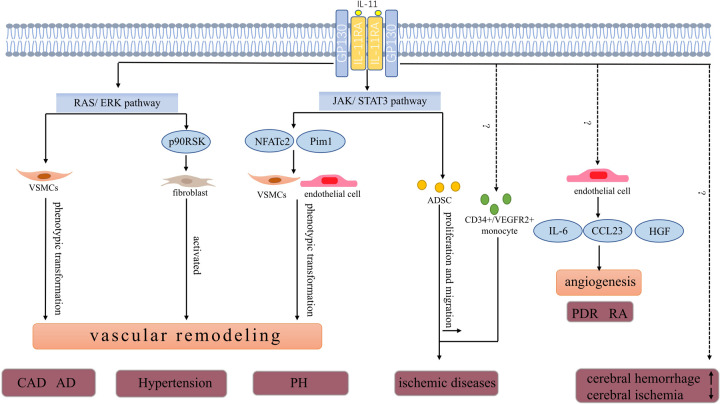
Figure 1.
Pathophysiologic roles of IL-11 in vascular diseases. IL-11 is involved in the progression of CAD. High IL-11 expression may increase the risk of developing restenosis after stent implantation. In a model of carotid artery plaque formation, IL-11 induces phenotype transformation of VSMCs by activating the ERK signal and promotes vascular fibrosis and plaque formation. AD is a fatal vascular disease the level of IL-11 in plasma and thoracic aorta with acute thoracic aortic dissection increased. IL-11 potentially stimulates phenotype transformation of VSMCs in an ERK-dependent manner. The phenotype transformation of VSMCs further promotes aortic remodeling and increased risk of aortic dissection. IL-11 promotes the development of hypertension and may also be associated with the ERK pathway. As discussed in the text, the expression of IL-11 and IL-11RA was upregulated in the pulmonary artery and serum of patients with PH. The JAK/STAT3 pathway, a key downstream pathway of IL-11, promotes pulmonary vascular remodeling by increasing the expression of Pim1 (a proto-oncogene serine/threonine protein kinase) and NFATc2 in endothelial and VSMCs. IL-11 level was positively correlated with the risk of developing cerebral hemorrhage and negatively correlated with the severity of cerebral ischemia.In ischemic diseases,IL-11 increases the number of circulating CD34+/VEGFR2+ monocytes, which ultimately improves blood supply. In addition, ADSCs promote angiogenesis in ischemic tissues. IL-11 enhances ADSCs’ proliferation and migration through the STAT3 signaling pathway to increase blood perfusion. In PDR and RA, IL-11 is involved in angiogenesis by inducing the secretion of HGF, CCL23, and IL-6 in HUVECs.CAD, coronary artery disease; AD, aortic dissection; PH, pulmonary hypertension; PDR, proliferative diabetic retinopathy; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; ADSCs, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells; NFATc2, nuclear factor of activated T cells 2; CCL23, C-C motif chemokine ligand 23; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor.