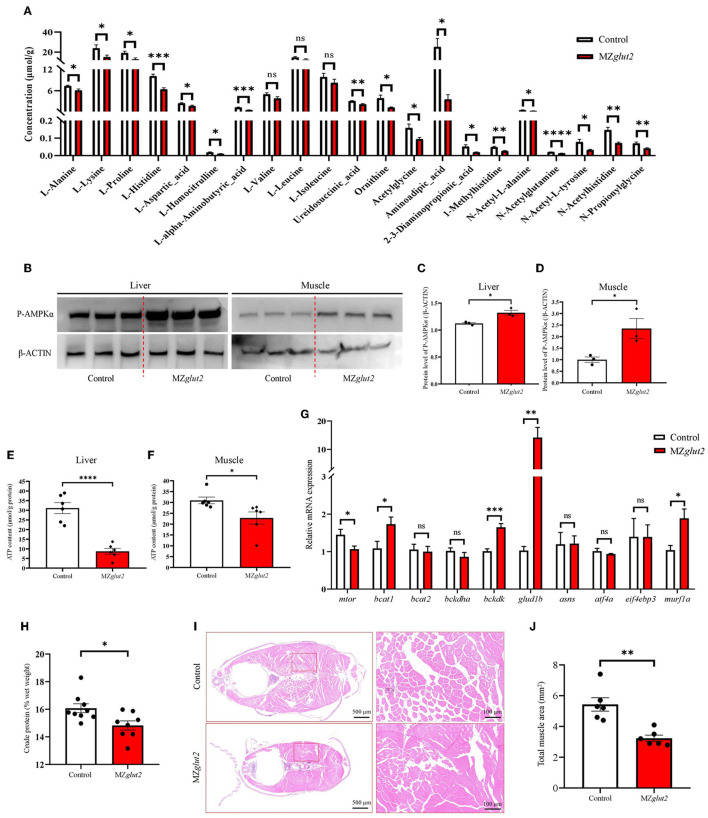
Figure 5.
glut2-deletion results in enhanced AMPK-mediated catabolic metabolism in MZglut2 fish. (A) The quantification of amino acid metabolites is based on the observations of metabolomics in the liver of the control and MZglut2 fish at 3 mpf (n = 6). (B–D) The level of P-AMPK and β-ACTIN proteins in the liver and muscle of the control and MZglut2 fish (n = 3). (E) The ATP content in the liver of control and MZglut2 fish (n = 6). (F) The ATP content in the muscle of the control and MZglut2 fish (n = 6). (G) The transcriptional expression levels of mtor, bcat1, bcat2, bckdha, bckdk, glud1b, asns, atf4a, eif4ebp3, and murf1a in muscle of control and MZglut2 fish at 3 mpf (n = 6). (H) The measurement of the crude protein content of the control (n = 9) and MZglut2 (n = 8) fish at 3 mpf. (I) Representative images of H&E staining of the control and MZglut2 fish at 3 mpf. (J) The bar chart represents the total area of muscle mass in the body cross-section (n = 6). A two-tailed unpaired t-test was used to detect significance. ****P < 0.0001.***P < 0.001. **P < 0.01. *P < 0.05. ns, no significance.