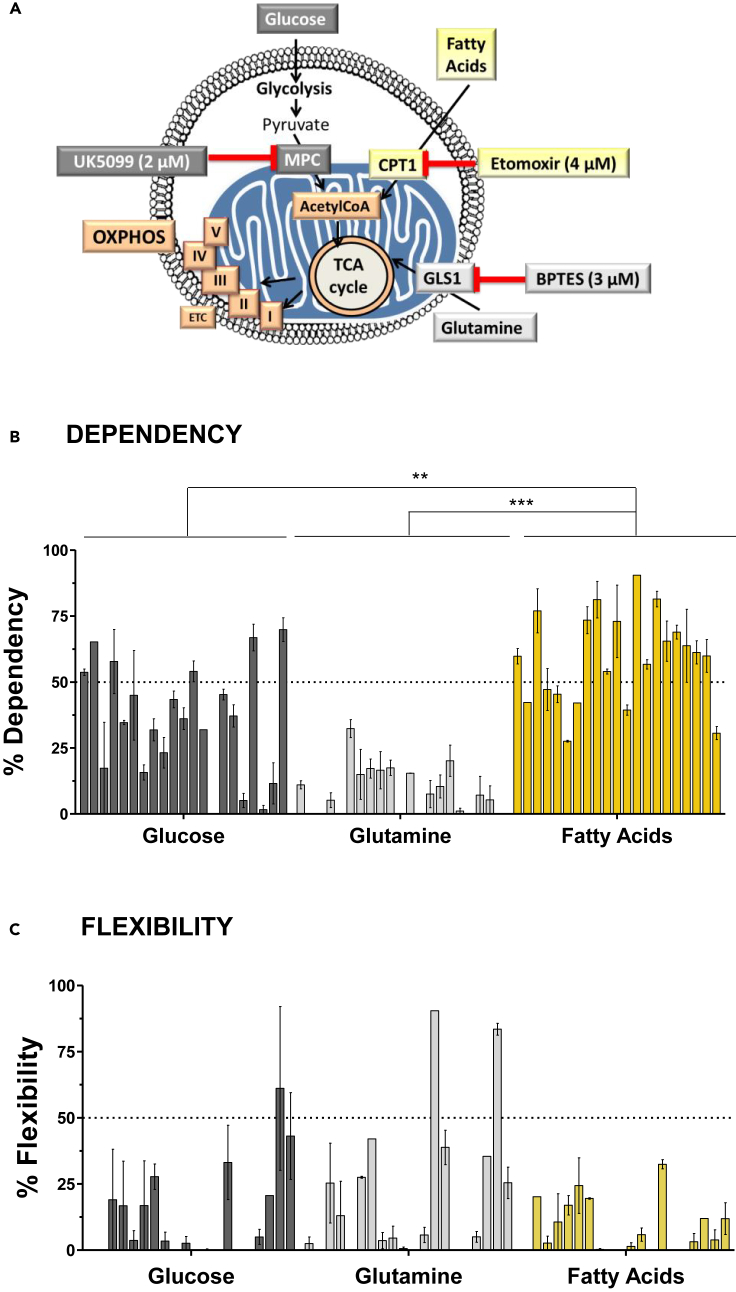
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial respiration of primary pancreatic cancer cells depends mainly on the fatty acid oxidation (FAO) pathway
(A) Schematic of Mito Fuel Flex Test carried out on the Seahorse analyzer. The rate of oxidation of glucose, glutamine, and long-chain fatty acids was determined by measuring the mitochondrial respiration (oxygen consumption rate). For this, specific inhibitors were used: UK5099 (2 μM), BPTES (3 μM), and Etomoxir (4 μM), to inhibit the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC), glutaminase 1 (GLS1), and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), respectively, and to determine glycolysis, glutaminolysis, and Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO), respectively.
(B and C) Percentage of dependency (B) and flexibility (C) of mitochondrial respiration to oxidize three main energetic fuels: glucose, glutamine, and fatty acids, in 21 primary PDAC cells from patients (each bar represents a patient). Data are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. p values were calculated from t test and Mann-Whitney test; ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.