Figure 1.
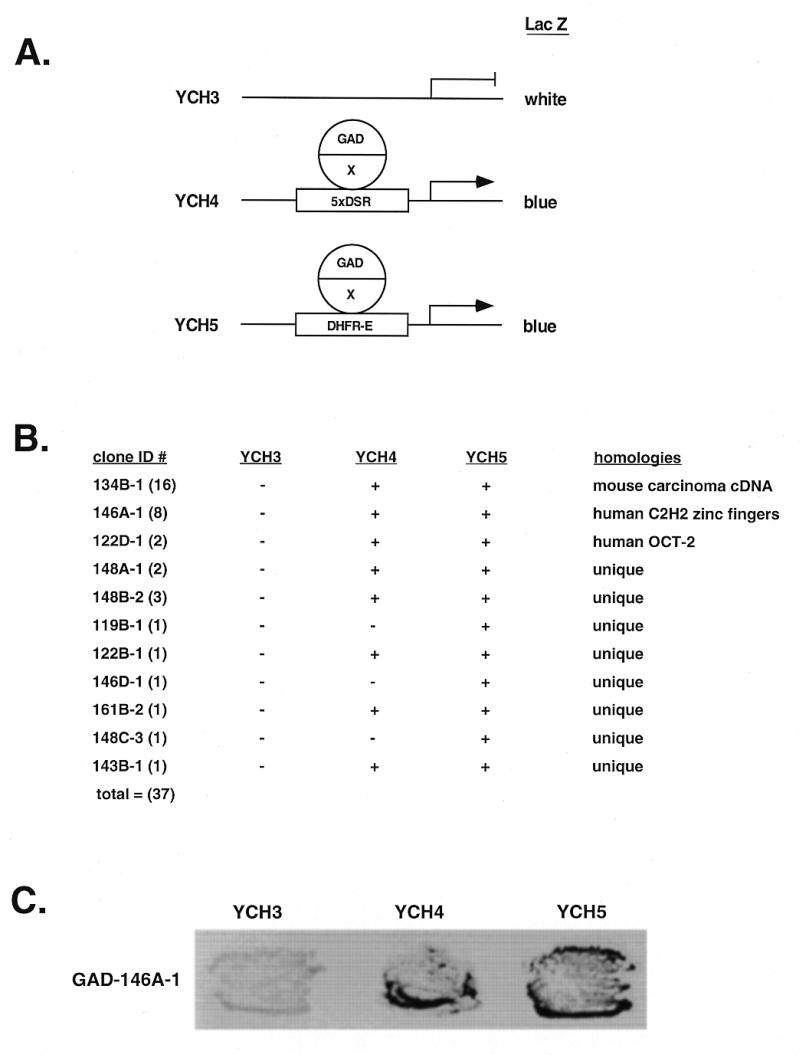
One hybrid screen in yeast for RIP60. (A) A genetic screen in S.cerevisiae was used to identify cDNA-encoded fusion proteins that bind the RIP60 target sequence (DSR) and activate expression of a linked reporter gene (LacZ or histidine) by recruiting a fused GAL4 activation domain (GAD) to the promoter. Shown are lacZ reporter strains in which lacZ expression is controlled by five copies of the DSR target sequence (YCH4) or a single copy of the DSR embedded in its native flanking sequences (YCH5). YCH3 was used as a control. (B) Summary of the one hybrid screen. From 14 million transformants, 37 clones were found that activated expression in YCH4 and/or YCH5 but not in YCH3. (C) Specificity test in yeast for RIP60 binding. In the one hybrid screen multiple in-frame fusions were identified that overlapped with clone 146A-1. Each of these fusions contained the Z2 and PRR region of RIP60 and activated lacZ expression in both YCH4 and YCH5, but not in YCH3.
