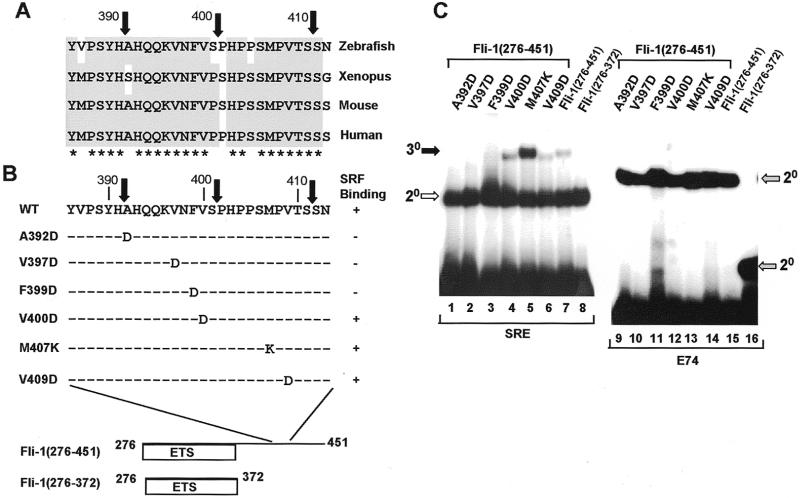
Figure 6.
Identification of important residues within the C-terminal SRF interaction motif. (A) Alignment of the sequences surrounding the truncation endpoints in Fli-1(276–391), Fli-1(276–401) and Fli-1(276–411) (indicated by black arrows) from zebrafish, xenopus, mouse and human homologues. Residues conserved in three or more species are shaded grey, and fully conserved amino acids are indicated by asterisks. (B) Location and identity of the amino acids mutated in zebrafish Fli-1. A summary of the results of the gel retardation assays is shown on the right. (C) Gel retardation analysis of complex formation by the indicated truncated and mutant Fli-1 derivatives in the presence of coreSRF(T196A) and the c-fos SRE (lanes 1–8) or in the absence of coreSRF on the E74 site (lanes 9–16). The locations of the ternary Fli-1–SRF–SRE (30, closed arrow), binary SRF–SRE (20, open arrow) and binary Fli-1–E74 (20, grey arrow) complexes are indicated.