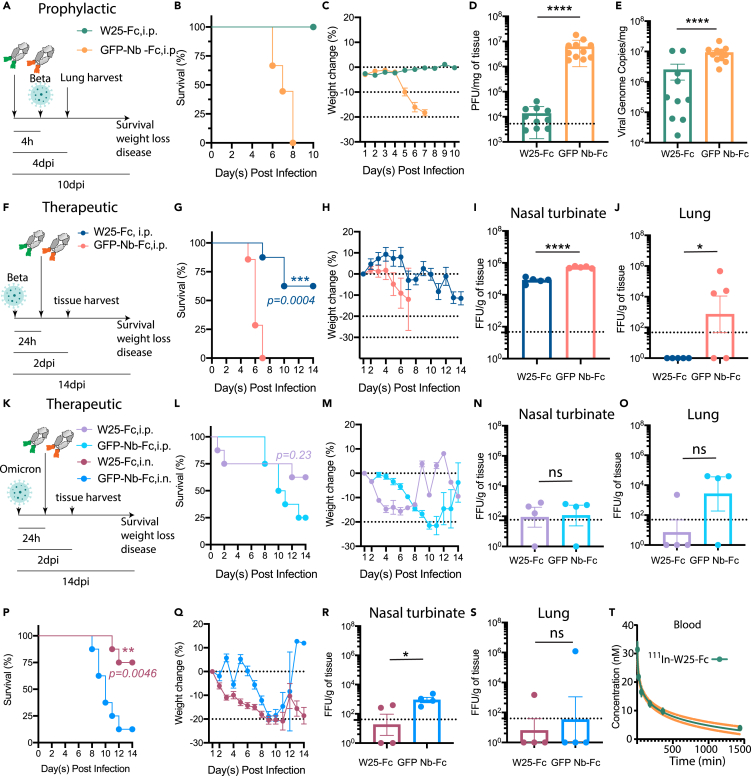
Figure 4.
W25-Fc protects mice from lethal Beta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 infection and W25-Fc pharmacodynamic analysis
(A) Experimental schematic: eight- to twelve-week-old male and female K18 transgenic mice were inoculated via the intranasal route with 1 × 103 PFU of SARS-CoV-2 (Isolate B.1.351). W25-Fc or GFP Nb-Fc were administered intraperitoneally 4 h prior to infection.
(B) Survival and (C) weight change were monitored and scored. Two experiments were performed (n = 9–12, Log rank (Mantel-Cox) test ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).
(D) Viral burdens were determined in lung tissues 4 day post infection via plaque forming assays for infectious virus and (E) RT-qPCR for viral genome copy number. Two experiments were performed (N = 10–11).
(F) Experimental schematic: five- to six-week-old female K18 transgenic mice were inoculated via the intranasal route with 1 × 104 FFU of SARS-CoV-2 (Beta, Isolate B.1.351) N = 8, and N = 4–5 each group for survival and tissue harvest experiment, respectively. For therapeutic treatment, W25-Fc or GFP-Nb-Fc were administered intraperitoneally 24 h after SARS-CoV-2 Beta infection at 5 × 103 FFU/mouse.
(G) Survival and (H) weight change were monitored. Viral loaded were determined in (I) nasal turbinate and (J) lung tissues 2 day post infection by immuoplaque assays for infectious virus.
(K) Experimental schematic: for Omicron infection, five- to six-week-old female K18 transgenic mice were inoculated via the intranasal route with 1 × 105 FFU of SARS-CoV-2 (Isolate B.1.1.529). W25-Fc or GFP-Nb-Fc were administered intraperitoneally or intranasally 24 h after infection.
(L and P) Survival and (M and Q) weight changes were monitored and scored. Viral loaded were determined in (N and R) nasal turbinate and (O and S) lung tissues 2 day post infection by immunoplaque assays for infectious virus. Bars represent medians, dots are individual animals, and dotted horizontal lines indicate the limit of detection. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(T) The pharmacodynamics of W25-Fc in blood was determined by conjugation of W25-Fc to radioactive 111Indium. One mg/kg were injected intravenously through the tail to 6 groups of mice (group 1: 5 min, group 2: 20 min, group 3: 60 min, group 4: 3 h, group 5: 5 h and group 6: 24 h). The mice were dissected, and concentration of 111In W25-Fc was measured in the blood using an Auto-Gamma Counter.