Figure 4.
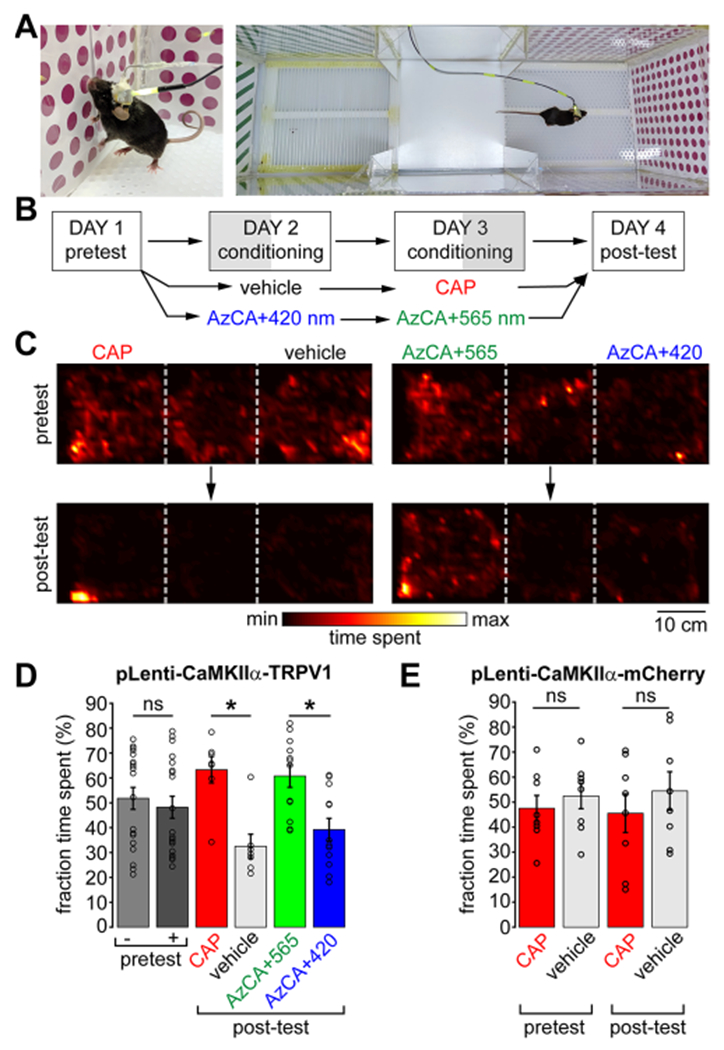
red-AzCA-4 enables light-dependent control of reward behavior in freely moving animals. (A) Awake and freely moving mice were connected to a microfluidic pump and LEDs and subject to a CPP test. (B) Timeline of the 4-day CPP test. (C) Heatmaps depicting the relative time spent at each position in the box for a representative mouse during the pretest (top) and after conditioning (post-test, bottom) with CAP/vehicle (left) or red-AzCA-4 + 420/565 nm irradiation (right). (D) TRPV1-expressing mice did not have a preference for either chamber during the pretest day (N = 19). Mice preferred the chamber where they received CAP over a vehicle control on the post-test day after conditioning (N = 7). Mice preferred the chamber where they received cis-red-AzCA-4 (green light) over trans-red-AzCA-4 (blue light) after their conditioning (N = 12). (E) Mice which only expressed mCherry and not TRPV1 did not develop a preference for the chamber associated with CAP delivery (N = 8). Error bars = mean ± SEM. * = P < 0.05; ns = not significant = P > 0.05.
