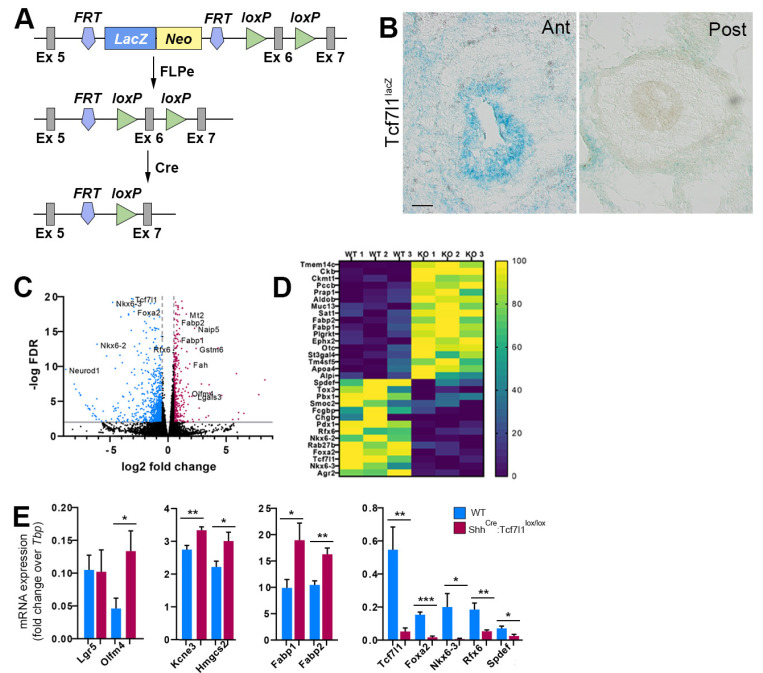
Figure 1.
Transcriptional changes in the embryonic intestinal epithelium in the absence of Tcf7l1. (A) The strategy used to generate Tcf7l1 conditional allele. Schematic representation of the “knockout-first” allele containing a splice acceptor: lacZ trapping cassette and a neo cassette inserted into the intron of a gene. After removal of the LacZ-neo cassette using Rosa26FLP recombinase, the “knockout-first” allele is converted to a conditional allele. Upon Cre mediated recombination the floxed exon 6 of the conditional allele is deleted, generating a frameshift mutation. (B) Transverse sections of the mouse small intestine from Tcf7l1lacZ embryos at E13.5 showing Tcf7l1 expression as revealed by β-galactosidase activity. Ant stands for anterior, Post stands for posterior. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) Volcano plot showing fold changes for genes differentially expressed between intestinal epithelial cells of Tcf7l1 mutant and wild type embryos at E13.5. Genes that were upregulated in Tcf7l1 mutants are shown in red. Genes that were downregulated in Tcf7l1 mutants are depicted in blue. (D) Heatmap showing top up- and down-regulated genes in Tcf7l1 mutant epithelial cells compared to controls. The annotation bar indicates normalized expression for each gene. (E) Quantitative RT-PCR analyses measuring the levels of stem cell markers (Lgr5, Olfm4, Kcne3 and Hmgcs2), enterocyte specific genes (Fabp1 and Fabp2), enteroendocrine (Foxa2, Nkx6-3, Rfx6), and goblet cell (Spdef) markers in wild-type (blue) and ShhCre-Egfp:Tcf7l1lox/lox (red) embryonic intestinal epithelium at E13.5. Values are normalized to the level of Tbp. Error bars are ±SD, n = 3 mice. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 according to two-tailed Student’s t-test.