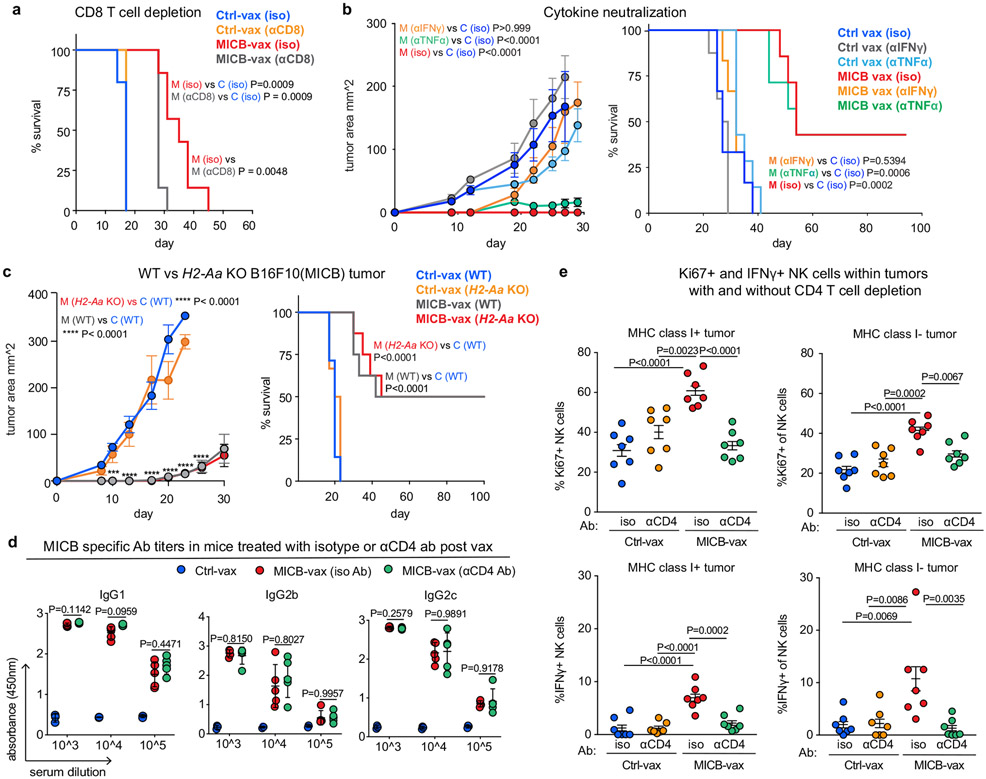
Extended Data Fig. 8 ∣. T cell and NK cell responses in MHC-I expressing and MHC-I deficient tumors.
a, Contribution of CD8 T cells to vaccine efficacy. Mice were first immunized with MICB-vax or Ctrl-vax (d0, d14), treated with either isotype control mAb, depleting mAb targeting CD8 T-cells starting on day 21, followed by implantation of B16F10 (MICB) tumor cells (n = 7 mice/group). b, Impact of IFNγ versus TNFα neutralization on the efficacy of the MICB α3 domain vaccine. MICB-transgenic mice received IFNγ or TNFα neutralizing mAbs or an isotype control mAb every 48 h, starting two days prior to subcutaneous injection of B16F10 (MICB) tumor cells on day 21 following immunization (n = 7 mice/group). Tumor growth (left) and survival analysis (right) are shown. c, Comparison of vaccine efficacy against B16F10 (MICB) wild-type tumors and tumors with resistance mutation in H2-Aa gene. Mice received MICB-vax (n=8 mice/ group) or Ctrl-vax (n = 7 mice/ group) and were then challenged with tumors of the indicated genotypes. d, Quantification of MICB-specific serum Ab titers in mice immunized with Ctrl-vax (blue) or MICB-vax followed by treatment with CD4 T-cell depletion (green) or control (red) mAbs for 3 weeks, starting on day 28 following immunization (n=5 mice/group). e, Impact of CD4 T-cell depletion on vaccine-induced NK cell infiltration into tumors. Flow cytometric quantification of the percentage of Ki67+ NK cells (top) and IFNγ+ NK cells (bottom) in WT (left) and B2m-KO (right) tumors for the following treatment groups: Ctrl-vax + isotype mAb (blue), Ctrl-vax + anti-CD4 (orange), MICB-vax + isotype mAb (red) and MICB-vax+anti-CD4 (green); (n = 7 mice/group). Representative data from two independent experiments (a-c, e). Data from a single experiment with technical triplicates (d). Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (a); two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (b left, c left) and Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (b right, c right); two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (d); one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (e).