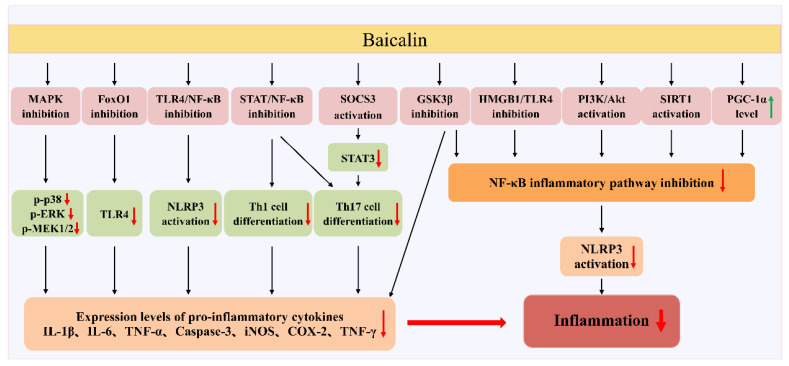
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of anti-inflammatory pathways induced by baicalin. (1) The anti-inflammatory effect of baicalin depends on reducing the expression of inflammatory factors that might be involved in the regulation of several signaling pathways, including MAPK, FoxO1, TLR4/NF-κB, signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)/NF-κB, and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3). (2) Baicalein inhibits NF-κB activation by activating phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) and sirtuin 1 (SIRTI) pathways and inhibiting the high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)/TLR4 signaling pathway. (3) Baicalin alleviates inflammatory responses by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammatory vesicle activation through negative regulation of the NF-κB pathway and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3 β) factor pathway.