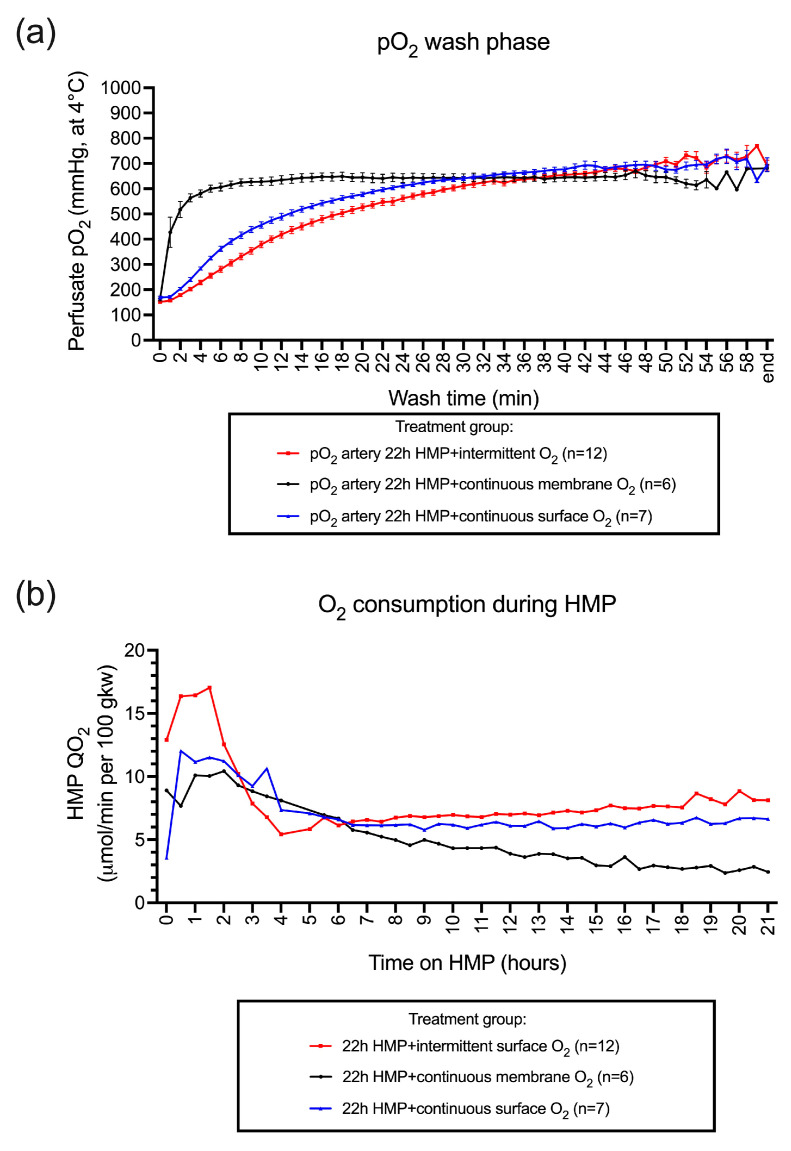
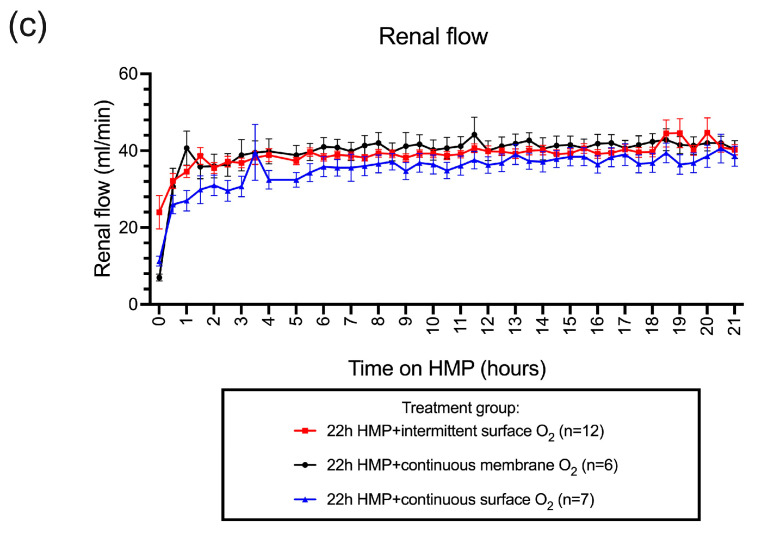
Figure 3.
The evolution of perfusate oxygen concentration, O2 consumption, and renal flow during hypothermic machine perfusion. To obtain perfusate pO2 levels above 500 mmHg (at 4 °C), before connecting the kidney to the perfusion device, short bubble oxygenation of minimum 15 min was demonstrated as efficient as membrane oxygenation (a). Both surface-oxygenated groups demonstrated oxygen consumption during the entire preservation period. In contrast, the membrane-oxygenated group demonstrated a decreasing trend of oxygen consumption starting after 2 h of machine perfusion (b). Active oxygenation, independent of the type of oxygen administration technique, demonstrated a comparable renal flow profile during the 22 h of machine perfusion (c).