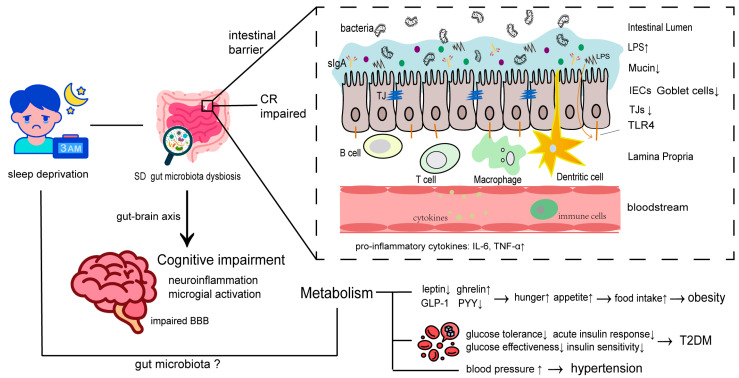
Figure 3.
Summary of SD-induced diseases and their relationships with SD-induced gut microbiota dysbiosis. In the immune system, SD gut microbiota disorders lead to broken intestinal barriers and impaired colonization resistance, which can manifest in decreased mucin, IECs goblet cells, TJs, and anti-inflammatory cytokines, as well as increased LPS and pro-inflammatory cytokines. In the metabolic system, SD contributes to obesity, T2DM, and hypertension; the effects of gut microbiota in this process have been fully characterized. In the nervous system, SD gut microbiota disorders result in decreasing functions of cognition via neuroinflammation and microglial activation. The up/down arrows indicate the increase/decrease of the represented object.