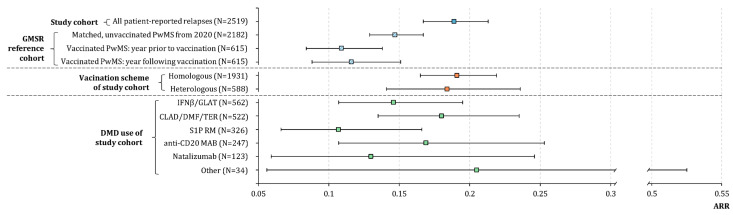
Figure 2.
(Extrapolated) annualized relapse rates following SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations in patients with multiple sclerosis stratified by vaccination scheme and disease-modifying drug use. The ARRs are visualized as boxes parallel to the x-axis, flanked by whiskers that define the 95% confidence interval. The ARR of the study cohort is 0.189 (95% CI: 0.167–0.213). Comparing ARRs of a smaller GMSR reference group in the year before vaccination with the year following vaccination reveals no significant difference (0.109 [95% CI: 0.084–0.138] vs. 0.116 [95% CI: 0.088–0.151]). Patients with a homologous vaccination scheme (total: 0.191 [95% CI: 0.165–0.219]│solely tozinameran: 0.180 [95% CI: 0.154–0.210]│solely elasomeran: 0.283 [95% CI: 0.195–0.398]│solely AZD1222: 0.161 [95% CI: 0.065–0.332]│insufficient patient number for Ad26.COV2.S [N = 22]) show a similar disease activity compared to those with a heterologous scheme (0.184; 95% CI: 0.141–0.236). Considering the different DMD groups, patients with CLAD/DMF/TER reveal the highest extrapolated ARR (0.180; 95% CI: 0.135–0.235), followed by those with anti-CD20 MAB (0.169; 95% CI: 0.107–0.253), IFNβ/GLAT (0.146; 95% CI: 0.107–0.195), natalizumab (0.130; 95% CI: 0.059–0.246), and S1P RM (0.107; 95% CI: 0.066–0.166). Patients with other DMDs (N = 31) have an extrapolated ARR of 0.205 but show a 95% CI of 0.056–0.525. anti-CD20 MAB—anti-CD 20 monoclonal antibody: ocrelizumab/ofatumumab/rituximab; ARR—annualized relapse rate; CLAD/DMF/TER—cladribine/dimethyl fumarate/teriflunomide; CI—confidence interval; DMD—disease-modifying drug; IFNβ/GLAT—interferon beta-1a/interferon beta-1b/peginterferon beta-1a/glatiramer acetate; MS—multiple sclerosis; N—number of patients; PwMS—people with MS; S1P RM—sphingosin-1-phosphate receptor modulator: fingolimod/ozanimod/siponimod; SARS-CoV-2—severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.