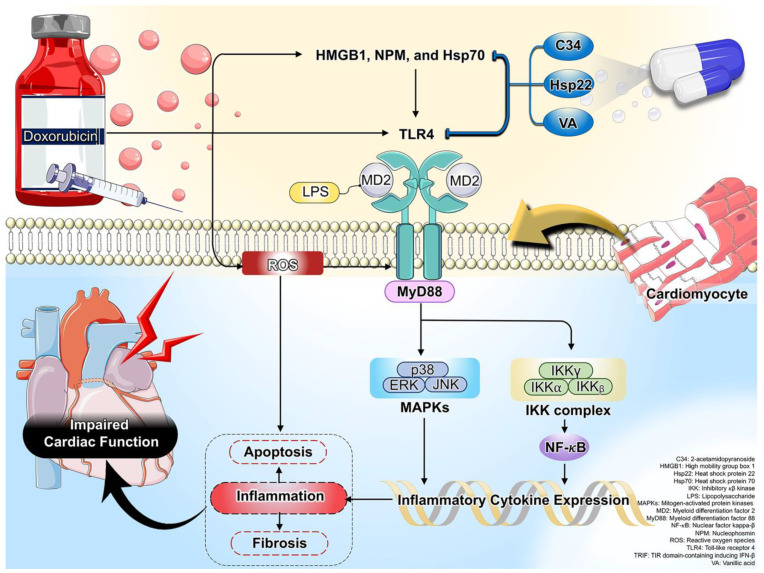
Figure 1.
A schematic presentation of oxidative stress and inflammation-related mechanisms via TLR4 in Dox-induced cardiotoxicity. Activation of TLR4 was exhibited by HMGB1, NPM, and Hsp70, leading to increased cardiac inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis, and impaired cardiac function in Dox treatment. Its subsequent detrimental effects were effectively attenuated by treatment with C34, Hsp22, and VA.