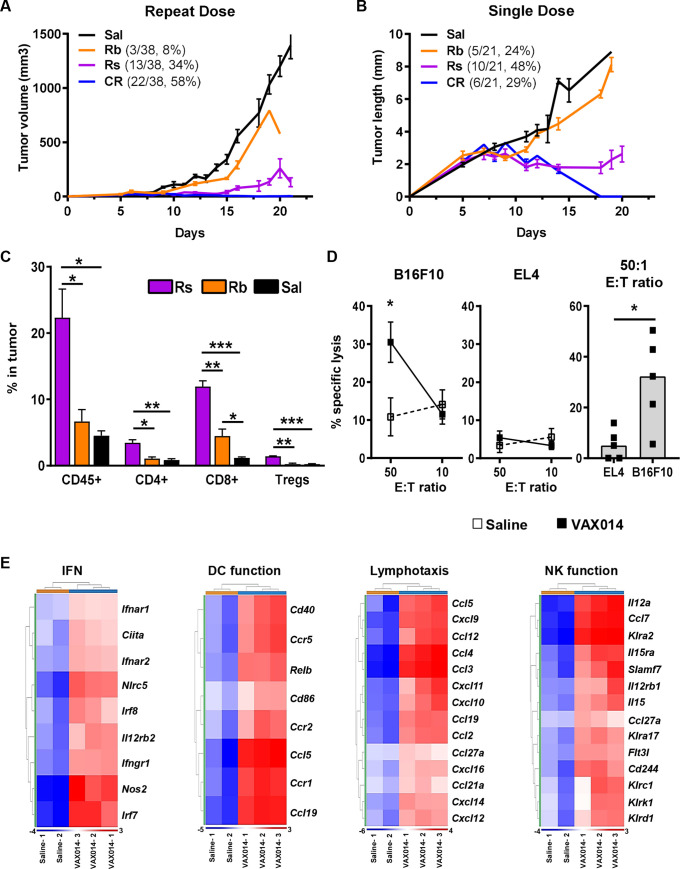
Figure 2.
Intratumoral administration of VAX014 increases TILs, upregulates multiple immune gene networks, and results in systemic tumor-specific cellular immunity. (A) Mean tumor growth rates of injected B16F10 tumors following weekly intratumoral treatment with saline (n=35) or VAX014 divided into disparate response groups defined as Rs, Rb, or CR. (B) Mean tumor growth rates of injected B16F10 tumors after a single lower intratumoral dose with saline (n=10) or VAX014 and divided into disparate response groups (described in A). (C) Percentage of total leukocytes (CD45+), CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs (CD4+Foxp3+) in actively responding B16F10 tumors versus rebounding and saline-treated tumors following a single intratumoral treatment with VAX014 (tumors analyzed by flow cytometry on days 20–28, n=3/group). (D) Splenic CTL activity against B16F10 target cells or EL4 non-specific haplotype matched control target cells following a single intratumoral treatment with VAX014 versus saline-treated control (splenocyte isolation/expansion performed on day 14 post tumor implantation, n=4–5/group). (E) Heatmaps of immune gene networks for IFN response, DC function, lymphotaxis, and NK function from immunotranscriptomes of B16F10 tumors 24 hours following intratumoral injection with VAX014 (n=3) versus saline-treated tumors (n=2). Statistical significance for mean CTL activity was analyzed using Student’s t-test, and median VAX014 CTL activity at 50:1 E:T ratio was analyzed using Mann-Whitney U test. Where present, error bars represent ±SEM. CR, complete response; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; DC, dendritic cell; E:T, effector-to-target; IFN, interferon; NK, Natural Killer cells; Rb, rebounding tumor; Rs, actively responding tumor; Sal, saline.