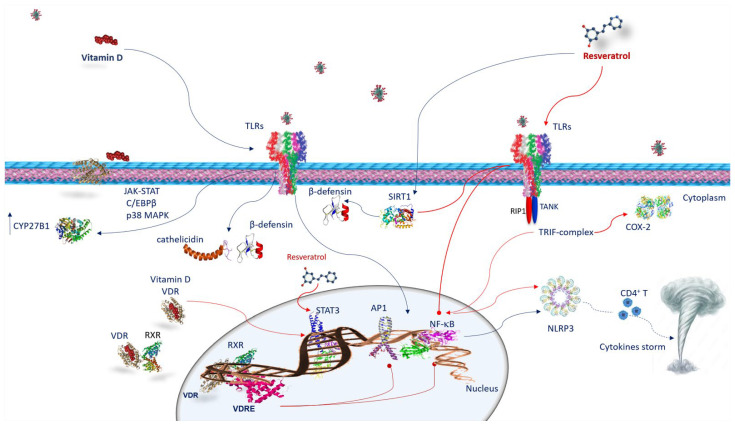
Figure 2.
Vitamin D and resveratrol immune response against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Vitamin D interacts with the cells of the innate immunity by activating TLRs and upregulating CYP27B1. The mechanism by which TLR binding improves CYP27B1 expression involves JAK-STAT, C/EBPβ, and p38 MAPK pathways. Following TLRs stimulation, vitamin D activates innate immunity, increasing cathelicidins and β-defensins. VDR is expressed in many immune cells. Once vitamin D is hydroxylated interacts with VDR, vitamin D/VDR complex negatively regulates STAT3. Vitamin D exerts its effects through genomic mechanisms modulated by VDR/RXR complex to bind to VDRE in target genes of immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, and T and B lymphocytes. VDRE promotes the recruitment of nuclear proteins in transcriptional-complex-modulating inflammatory response. Resveratrol acts against COVID-19 inhibiting TRIF signaling in the TLRs pathway by RIP1/TANK in the TRIF complex. It inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation. Resveratrol reduces COX-2 expression by preventing TRIF signaling. Resveratrol also activates the SIRT1 pathway, which disrupts TLR4/NF-κB/STAT signal, decreasing cytokine storm. Resveratrol-inducing SIRT1 can mediate β-defensins induction. Both vitamin D and resveratrol inhibit NF-κB and consequently, NLRP3 inflammasome, avoiding CD4+ T cell activation and cytokine storm. Abbreviations: AP1—activator protein 1; C/EBPβ—CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β; CD4T—CYP27B1, cytochrome P450 family 27 subfamily B member 1; COX2—cyclooxygenase-2; JAK-STAT—Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription; NF-κB—nuclear factor kappa B; NLRP3—NLR family pyrin-domain-containing 3; p38 MAPK—p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; RIP1—receptor-interacting protein; RXR—retinoid X receptor; SIRT1—sirtuin 1; STAT 3—signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TANK—TRAF family member-associated NFKB activator; TLR—Toll-like receptor; TRIF—TIR-domain-containing, adapter-inducing interferon-β; VDR—vitamin D receptor; VDRE—vitamin D response elements.