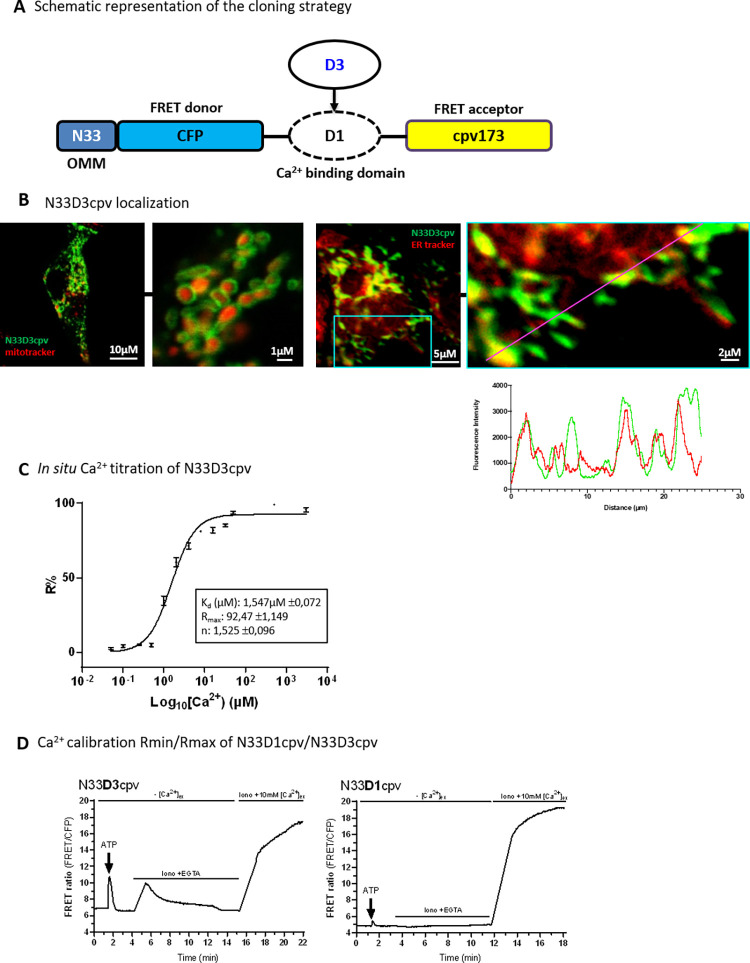
Fig 1. Characterization of N33D3cpv.
(A) Schematic representation of the cloning strategy. Original Ca2+ biosensor N33D1cpv is composed of a signal addressing sequence (N33) coding for an outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) peptide, the FRET donor (CFP: Cyan Fluorescent Protein), the Ca2+-binding domain D1 and the FRET acceptor (cpv173: circularly permutated venus protein). N33D3cpv was generated by replacing D1 Ca2+-binding domain with the D3 domain. (B) (left panel) Confocal images of H9c2 cell expressing N33D3cpv biosensor (green) and stained with a mitochondrial marker (mitotracker deep red). (right panel) Confocal images of H9c2 cell expressing N33D3cpv biosensor (green) and stained with an ER marker (ER tracker red). Line scan analysis of fluorescent intensity of green (N33D3cpv) and red fluorescence (ER tracker) (right panel). Zoomed-in panel for this analysis is represented on the original image by a blue square. (C) In situ Ca2+ titration assay of N33D3cpv with the fit values shown in the box. Data plotted: mean ± SEM (n ≥ 9) cells for each [Ca2+]. (D) Representative kinetics of FRET ratio (FRET/CFP) of H9C2 cells stimulated with 100μM ATP in Ca2+ free extracellular medium then permeabilized with ionomycin (5μM) in an intracellular medium containing EGTA (600μM) and BAPTA-AM (5μM) then finally perfused with an intracellular medium containing CaCl2 (10mM). (Left panel) N33D3cpv. (Right panel) N33D1cpv. Raw values of FRET ratio are presented (FRET canal/CFP).