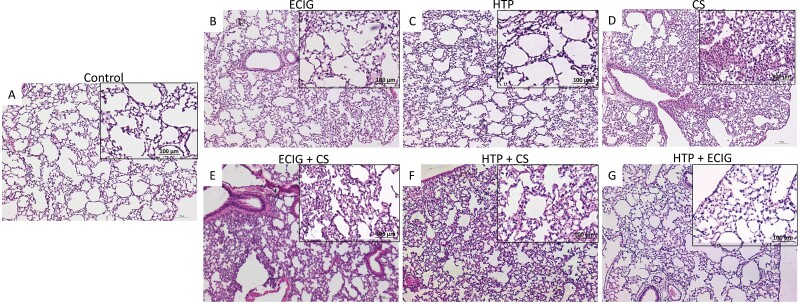
Figure 2.
H&E examination under light microscopy of lung tissues from (A) Control, (B) ECIG, (C) HTP, (D) CS, (E) ECIG + CS, (F) HTP + CS, and (G) HTP + ECIG. Original magnification: ×40. Lung issues of two-month-old male C57BL/6 mice were examined. A: Normal mouse lung showing thin interstitial alveolar wall and fine capillary vessels. B & C: After one week of days of exposure to (ECIG) or HTP, rare inflammatory cells, minimal injury, damage to the lung parenchyma, and preservation of pulmonary alveoli are observed. D: CS exposure is associated with a significant influx of inflammatory cells with thickened alveolar walls and destruction of alveolar spaces. E & F: ECIG +CS and HTP + CS demonstrated milder forms of lung injury when compared to CS exposure. HTP + ECIG No evidence of lung injury was observed. Insets represent magnified images; Scale bar 100 μm.