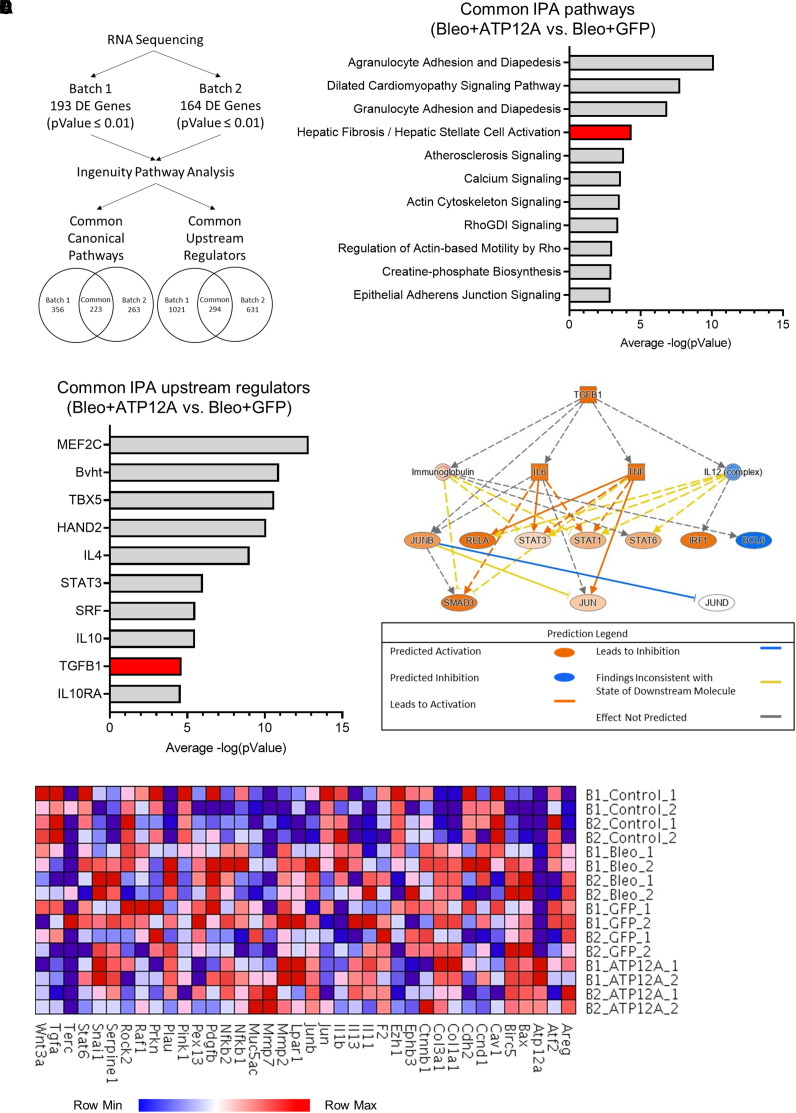
Figure 4.
Viral vector–mediated ATP12A expression in mouse lungs enhanced fibrotic pathway and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) signaling pathway in BLEO-induced pulmonary fibrosis. (A) Diagram showing the data analysis workflow. Data was collected from the bulk RNA sequencing of mouse lung tissue after treatment with BLEO and the adenovirus-mediated expression of GFP or ATP12A. Sequencing and differential expression analysis were performed on two batches of samples (P = 0.01). The lists of differentially expressed genes were submitted to QIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) to identify canonical pathways and upstream regulators. (B) The common canonical pathways from the BLEO and ATP12A versus BLEO and GFP comparison in each batch were compiled and arranged according to the average −log(value), as calculated by IPA. The hepatic fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation pathway is highlighted in red. (C) Common upstream regulators were identified between the BLEO and ATP12A versus BLEO and GFP comparison in the two batches and arranged on the basis of the average −log(pValue) calculated by IPA. The TGF-β1 upstream regulator is highlighted in red. (D) Pathway diagram displaying the predicted activation states of molecules in the TGF-β1 signaling pathway based on differential gene expression data submitted to IPA. (E) Heatmap displaying the expression levels of selected genes from the IPF pathway, as listed by IPA, as well as genes of interest included by the authors (Atp12A and Muc5ac).