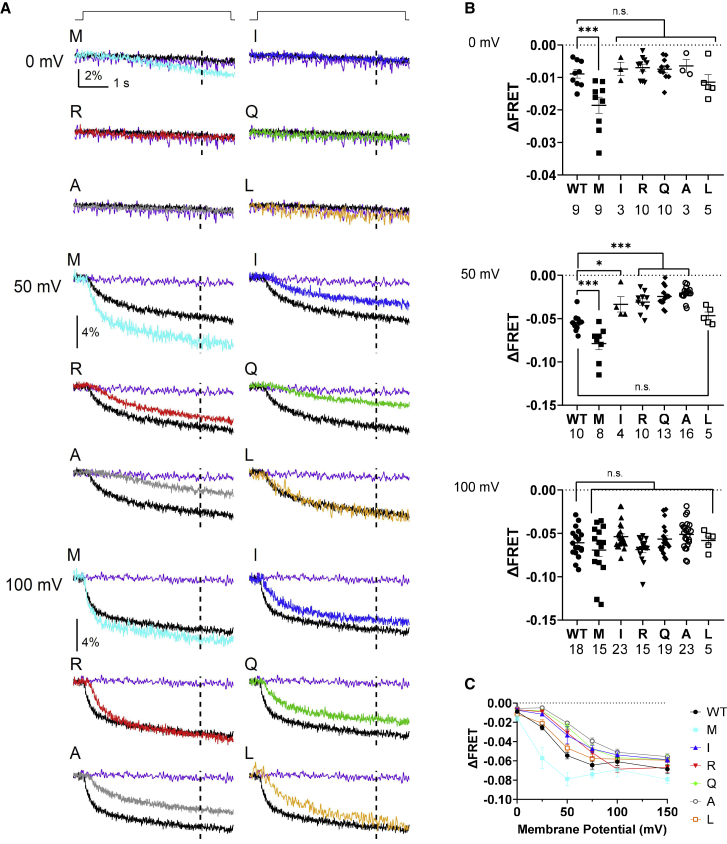
Figure 4.
Voltage-dependent PI(4,5)P2 phosphatase activity of Ci-VSP K364 mutants by VCF analysis with F-PLC, a PI(4,5)P2-selective FRET probe, in Xenopus oocyte. (A) Representative traces of F-PLC YFP/CFP ratio signal measured at 0 mV (top), 50 mV (middle), and 100 mV (bottom). Depolarizing step shown at top of traces was applied from a holding potential of −60 mV to indicated value for 5 s. Dotted line in each trace indicates the time point (at 4 s after the beginning of depolarization) for calculating ΔFRET. Signal from oocytes with WT Ci-VSP and without Ci-VSP is shown as black and purple trace, respectively. (B) FRET signal as the shift from the baseline measured at 4 s after initiation of step at 0mV (top), 50 mV (middle), and 100 mV (bottom). The number of recordings is shown for WT and mutants. (C) Plot of deviations of standardized FRET signal from the baselines against pulse voltage. Data at 25, 75, and 150 mV are shown in Fig. S6. Each trace from 0 to 150 mV was obtained from the same oocytes. In (B) and (C), data are presented as mean ± SE. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; n.s., statistically not significant, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. Sample size is as described in (B) and Fig. S6B.