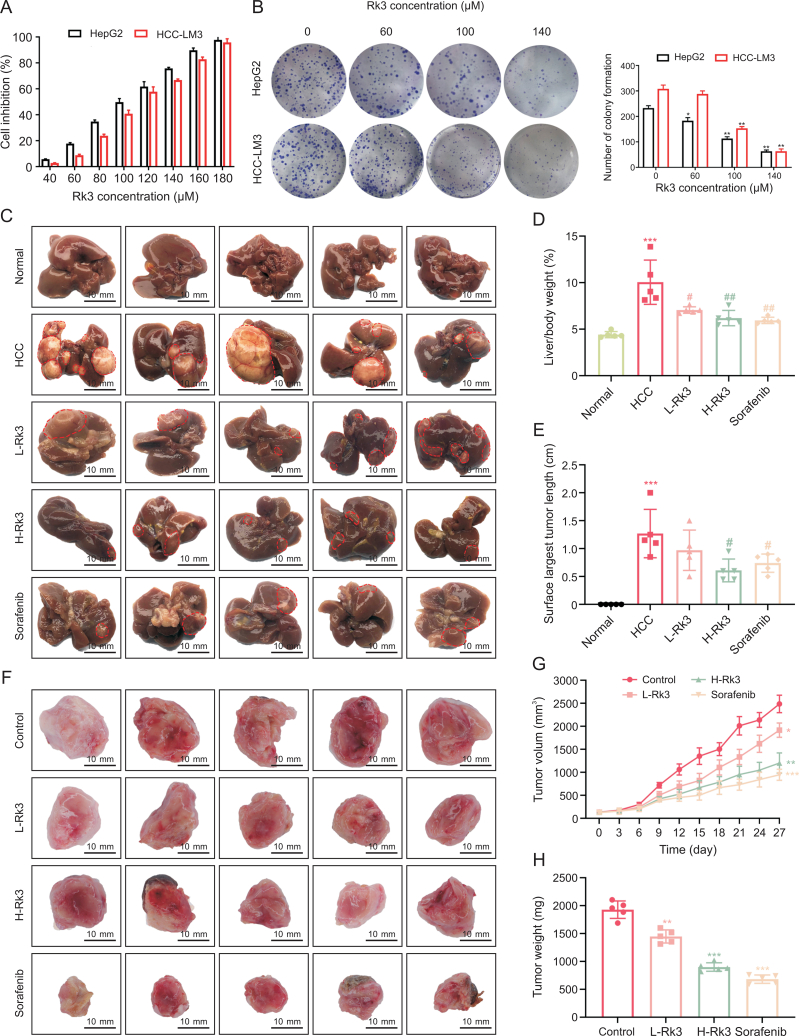
Fig. 2.
Ginsenoside Rk3 inhibited the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) both in vitro and in vivo. (A) Cell viability of HepG2 and HCC-LM3 treatment with ginsenoside Rk3. (B) Clone formation of HepG2 and HCC-LM3. (C) Anatomy of the liver of a mouse with primary liver cancer. (D) Liver to body weight of a mouse with primary liver cancer. (E) The surface largest tumor length of a mouse with primary liver cancer. (F) Tumor anatomy of HCC-LM3 subcutaneous tumor-bearing mice. (G) Tumor volume of HCC-LM3 subcutaneous tumor-bearing mice. (H) Tumor weight of HCC-LM3 subcutaneous tumor-bearing mice. L-Rk3: 50 mg/kg Rk3; H-Rk3: 100 mg/kg Rk3; sorafenib: 100 mg/kg. Data are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD). ∗P < 0.05 compared with the normal or control group, ∗∗P < 0.01 compared with the normal or control group, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with the normal or control group, #P < 0.05 compared with the HCC group, ##P < 0.01 compared with the HCC group.