Fig. 3.
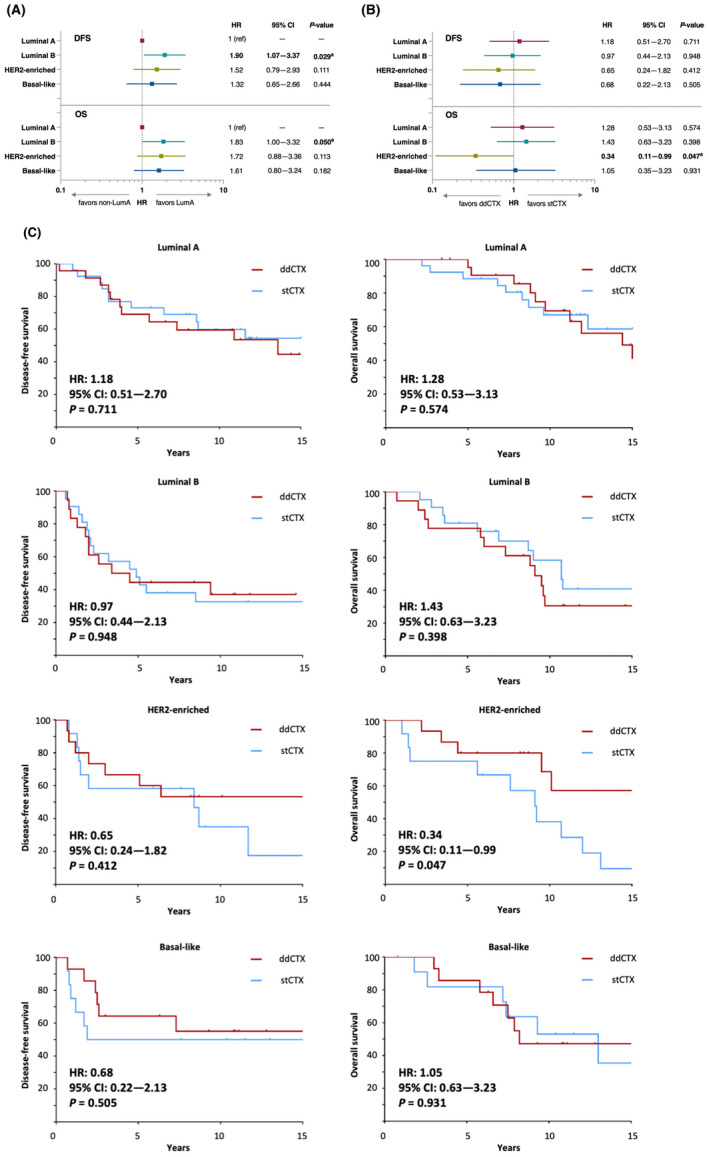
Intrinsic subtype of tumors is found to have prognostic and predictive association with survival outcomes. (A) In comparison with patients with Luminal A tumors, patients with other intrinsic subtypes had poorer survival outcomes which were statistically significant in patients with Luminal B tumors. (B) ddCTX showed a better treatment effect in comparison with stCTX in patients with HER2‐E tumors, (C) as seen also in the Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of the OS in these patients. Multivariate analyses were performed only for variables with significant unadjusted P values either for treatment‐by‐gene/signature interaction or for treatment effect within a gene/signature subgroup. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were analyzed using Cox regression analysis and Wald test. Statistically significant associations in (A) and (B) are shown in bold. a P‐value < 0.05 following multivariate analyses adjusting for age (< 43 versus ≥ 43 years), pT stage (T1 versus T2 versus T3 versus T4), number of involved nodes (4–9 versus > 9) and hormone receptor status (positive versus negative). CI, confidence interval; ddCTX, dose‐dense chemotherapy; DFS, disease‐free survival; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor‐2; HR, hazard ratio; OS, overall survival; stCTX, standard dose chemotherapy.
