Figure 6.
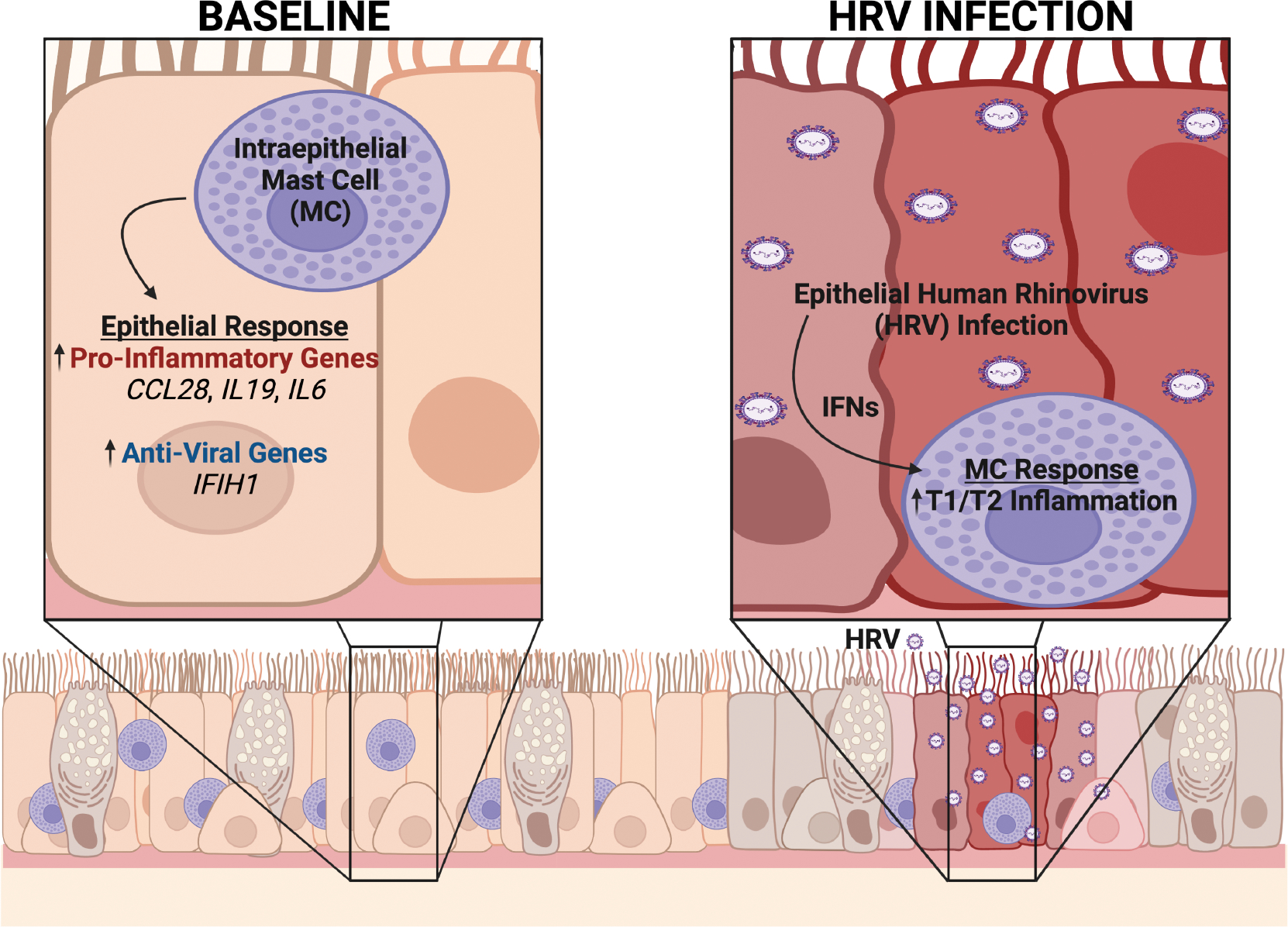
Ex vivo coculture modeling suggests bidirectional communication between airway epithelial cells (AECs) and mast cells (MCs) within the epithelial compartment in asthma. At baseline, MCs reside within the airway epithelium in asthma and our transcriptomic analyses suggest that MCs induce epithelial expression of pro-inflammatory and anti-viral genes. However, following human rhinovirus (RV) infection, epithelial-derived interferons enhance MC type-1 (T1) and type-2 (T2) immune responses. Figure created with biorender.com.
