FIGURE 4.
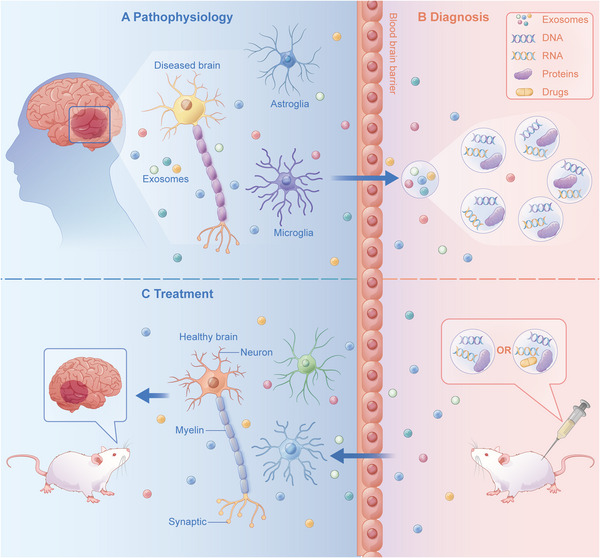
(A) Exosome crossing: exosomes from diseased nerve cells cross the blood–brain barrier and enter the peripheral circulation, releasing their contents such as RNA and protein; (B) extraction and modification of exosomes: exosomes are extracted from body fluids. Their contents are analyzed by high‐throughput sequencing qRT‐PCR and quantitative analysis tools to find clinical biomarkers, diagnose and predict the occurrence and development of diseases, provide a basis for clinical decision‐making, and identify and develop treatments based on exosome contents, such as increasing or decreasing a specific substance, or introduce therapeutic drugs, modify exosomes into engineered exosomes, and inject the engineered exosomes into model animals; (C) therapeutic effects of exosomes: engineered exosomes carrying therapeutic substances enter model animals, cross the blood–brain barrier, and reach the center to play a therapeutic role and restore nerve cell health.
