Figure 4: The overlapping glucagon-like peptide 1 signalling and insulin signalling pathways in neurons.
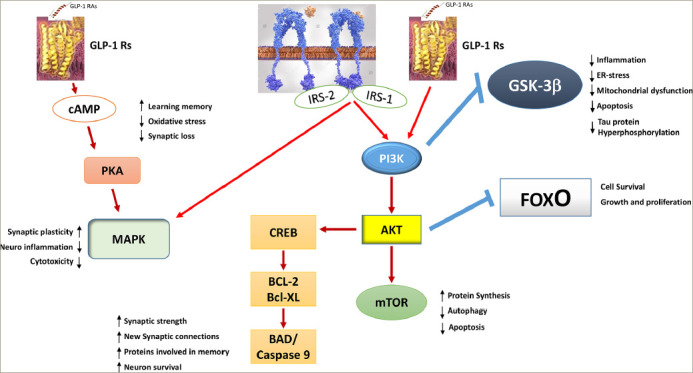
The activation of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptors activates protein kinase A (PKA) through adenosine cyclase and increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels. The downstream common pathways with insulin are phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) and mitogen-activated kinase pathways. The activation of GLP-1 receptors, therefore, increases insulin sensitivity and compensates for impaired insulin signalling. Tau hyperphosphorylation is reduced along with neurofibrillary tangle and beta-amyloid deposits.
AKT = protein kinase B; BAD = BCL-2 antagonist of death; BCL-2 = B cell lymphoma 2; Bcl-XL = B cell lymphoma extra-large; cAMP = cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB = cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein; ER = endoplasmic reticulum; FoxO = forkhead box O; GLP-1 RAs = glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists; GSK-3β = glycogen synthase kinase 3β; IRS = insulin receptor substrate; MAPK = mitogen-activated kinase; mTOR = mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K = phosphoinositide-3 kinase; PKA = protein kinase A.
