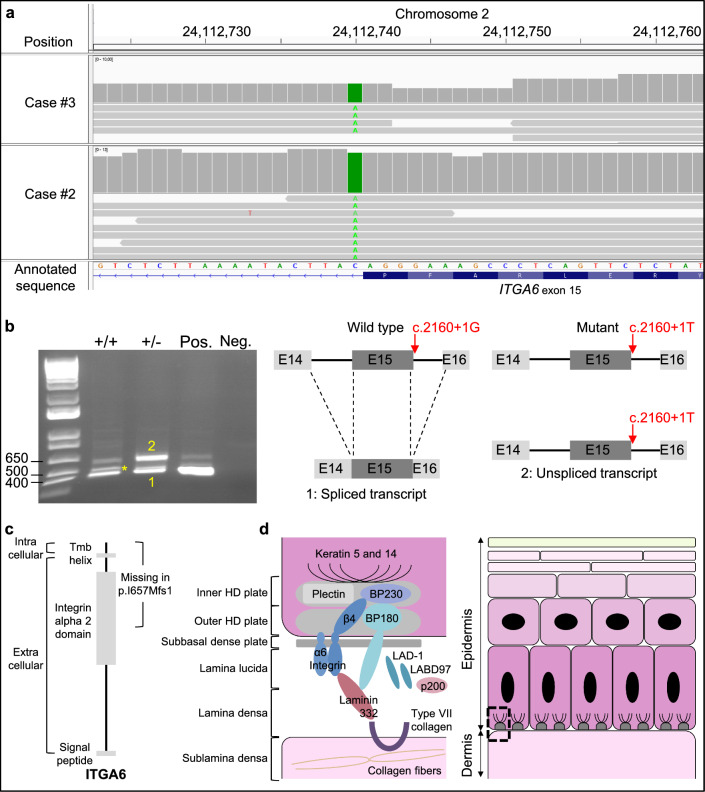
Fig. 2.
Identification of a splice site mutation in the ITGA6 gene and characterisation of its effects. a) IGV screenshot showing read coverage (up) and sequences (down) for cases #2 and #3 around variant Chr2 g.24112740C > A (ITGA6 c.2160 + 1G > T). b) Analysis of the consequences of this variant on the splicing of ITGA6. Left) Agarose gel electrophoresis after RT-PCR on negative control (Neg., water), positive control (Pos., commercial bovine muscle RNA), and ear biopsies RNA from one homozygous wild type (+/+) and one heterozygous carrier (+/-) of the mutation. *note the presence of a third band corresponding to partially spliced transcripts following the excision of either intron 14 or intron 15. Right) Details for the amplified segments after verification using Sanger sequencing. Boxes E14, E15, E16 correspond to exons 14 to 16. c) scheme of the wild type (Wt) and mutant ITGA6 proteins with domain information. Tmb Helix) transmembrane Helix. d) Structure of the hemidesmosomes (HD) and the dermo-epidermal zone (adapted from [27–29]). Note that BP180 is also known as COL17A1 and that laminin 332 is composed of LAMA3, LAMB3, and LAMC2