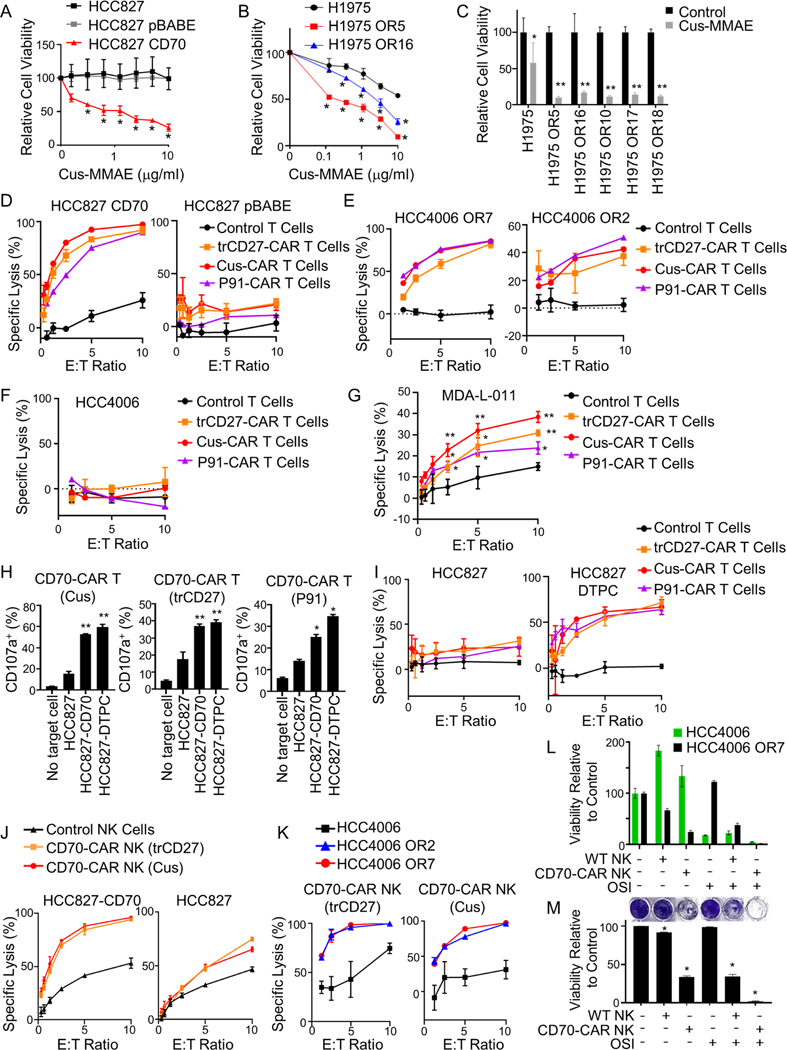
Figure 6. CD70 expression can targeted in EGFR TKI resistant cells.
(A) HCC827 cells with or without CD70 expression treated with cusatuzumab (Cus)-MMAE. *p ≤ 0.01. (B) H1975 and OR cells treated with cusatuzumab-MMAE. *p ≤ 0.01. (C) Viability of H1975 and OR variants treated with cusatuzumab (Cus)-MMAE (3 μg/ml). *p < 0.5; **p < 0.0007. (D - G) Activity of CD70 CAR T cells against HCC827 cells with or without CD70 expression (D), HCC4006 OR cells (E), HCC4006 parental cells (F), or MDA-L-011 cells (G). *p < 0.01; *p < 0.001. (H) CD107a expression on CD70 CAR T cells following incubation with HCC827 cells, HCC827 cells expressing CD70, and DTPCs. *p < 0.01; *p < 0.001. (I) Activity of CD70 CAR T cells against HCC827 cells and HCC827 DTPCs. (J &K) Activity of CD70-targeting CAR NK cells against HCC827 cells with or without CD70 (J) or HCC4006 parental cells and HCC4006 OR variants (K). (L & M) Viability (L) and clonogenic growth (M) of HCC4006 (GFP+) and HCC4006 OR7 (GFP-) cells grown as a mixed culture and treated with CD70-CAR NK (trCD27) cells, and osimertinib (OSI; 200 nM). *p < 0.0001. For all graphs, data shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistics were applied using multiple t tests (A, B, C), Student’s t test (H), or one-way ANOVA (M).
See also Figures S4 and S5.