Figure 6: Biochemical Pathways and Mitochondria.
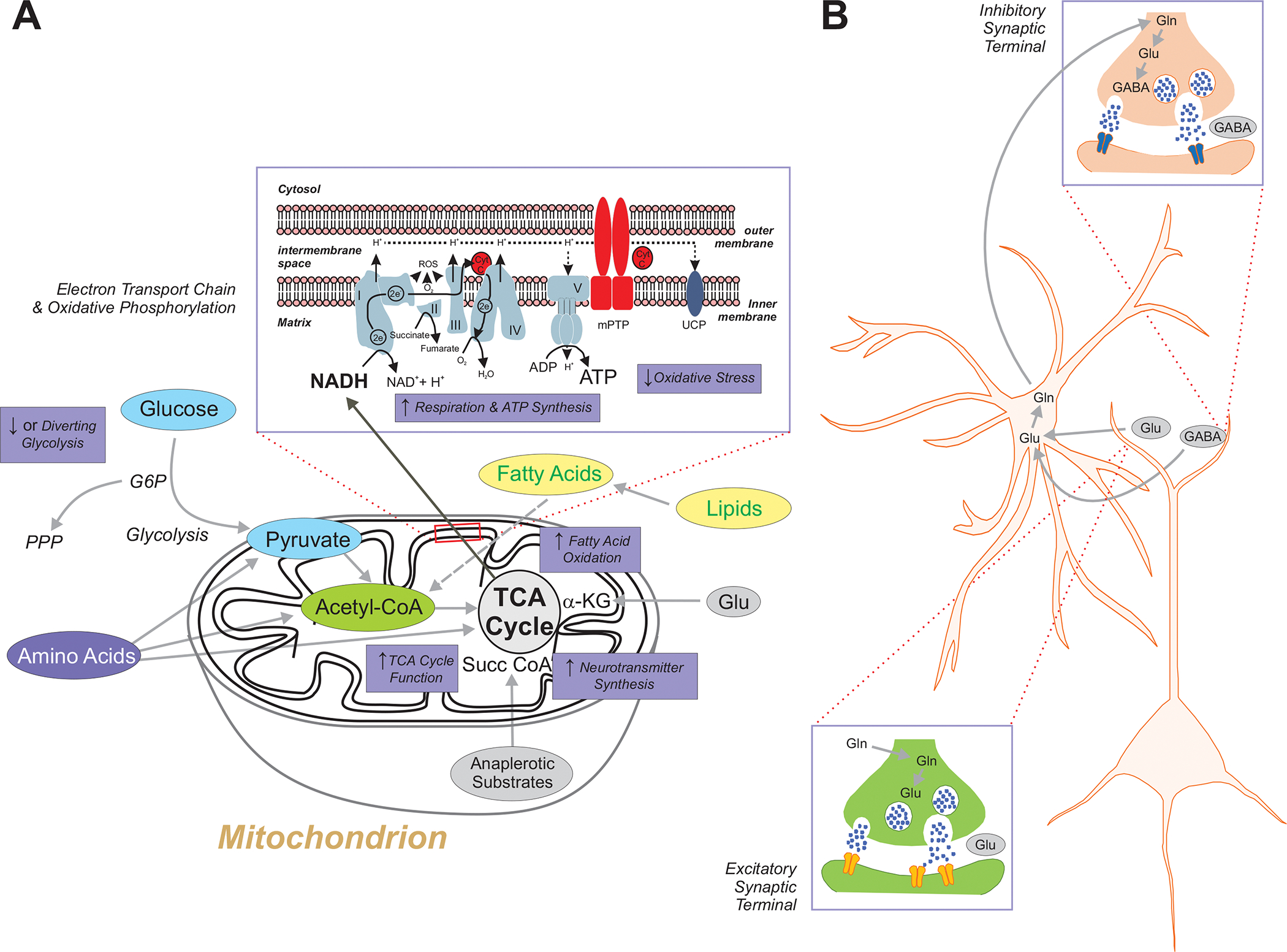
A. The biochemical effects of metabolic anti-seizure treatments have been linked in one way or another to the control of seizures or epilepsy in various experimental models. Inhibition of glycolysis with 2-deoxy-d-glucose results in seizure control in multiple animal models. Additionally, the glycolytic intermediate fructose-1,6-bisphosphate has been shown to exert broad anti-seizure effects, possibly by augmenting the pentose phosphate pathway. All amino acids can be converted for energy utilization if required, and can be glucogenic, ketogenic or both depending on where they enter certain biochemical pathways. For example, alanine, glycine and tryptophan can be converted to pyruvate, leucine and tryptophan to acetyl-coA, and histidine and glutamate into alpha-ketoglutarate of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Fatty acids derived from lipids can undergo fatty acid oxidation within the mitochondrial matrix and generate acetyl-CoA which can be condensed into acetoacetyl-CoA which is a precursor for the synthesis of acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate. Ketones are not only utilized for ATP production, but they can also be used for the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA. Certain fatty acids also enhance mitochondrial uncoupling protein (UCP) activity which partially dissipates the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane and as a result reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) production. Triglycerides such as triheptanoin provide anaplerotic substrates that when subsequently metabolized to succinyl CoA in mitochondria can also render anti-seizure effects. Finally, whether through the ketogenic diet (ketogenic diet) or ketone bodies, or through oxidative metabolism, mitochondrial respiratory chain function is enhanced – with resultant increases in oxygen consumption and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, and a reduction in oxidative stress. Inset: detailed view of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, and the five respiratory chain complexes denoted in Roman numerals. B. The glutamine-glutamate cycle between neurons and astrocytes is critical for the presynaptic biosynthesis of GABA, as well as providing glutamate that is converted by glutamate dehydrogenase to α-ketoglutarate which enters the TCA cycle as an intermediate87. Abbreviations: NAD+/NADH, oxidized/reduced forms of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; CytC, cytochrome C; G6P. glucose 6-phosphate; mPTP, mitochondrial permeability transition pore; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; UCP, mitochondrial uncoupling protein; Gln, glutamine; Glu, glutamate; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid;
