FIGURE 3.
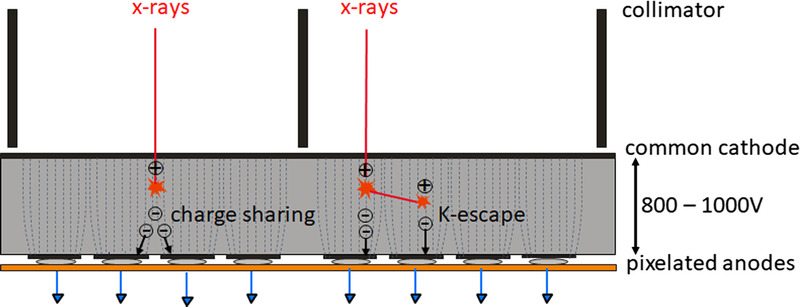
Schematic illustration of charge sharing and K-escape that reduce the energy separation of a realistic PCD. X-rays absorbed close to pixel borders produce electrons that generate signals in neighboring pixels (charge sharing). Thus, an x-ray photon is erroneously counted several times with too low energy. Incident x-rays can also initially knock out inner shell electrons from the detector material (K-electrons). This produces fluorescence radiation, which is reabsorbed and counted in the detector cell itself or in neighboring detector cells (K-escape). The incident x-rays at the primary interaction site are counted with too low energy.
