FIGURE 3.
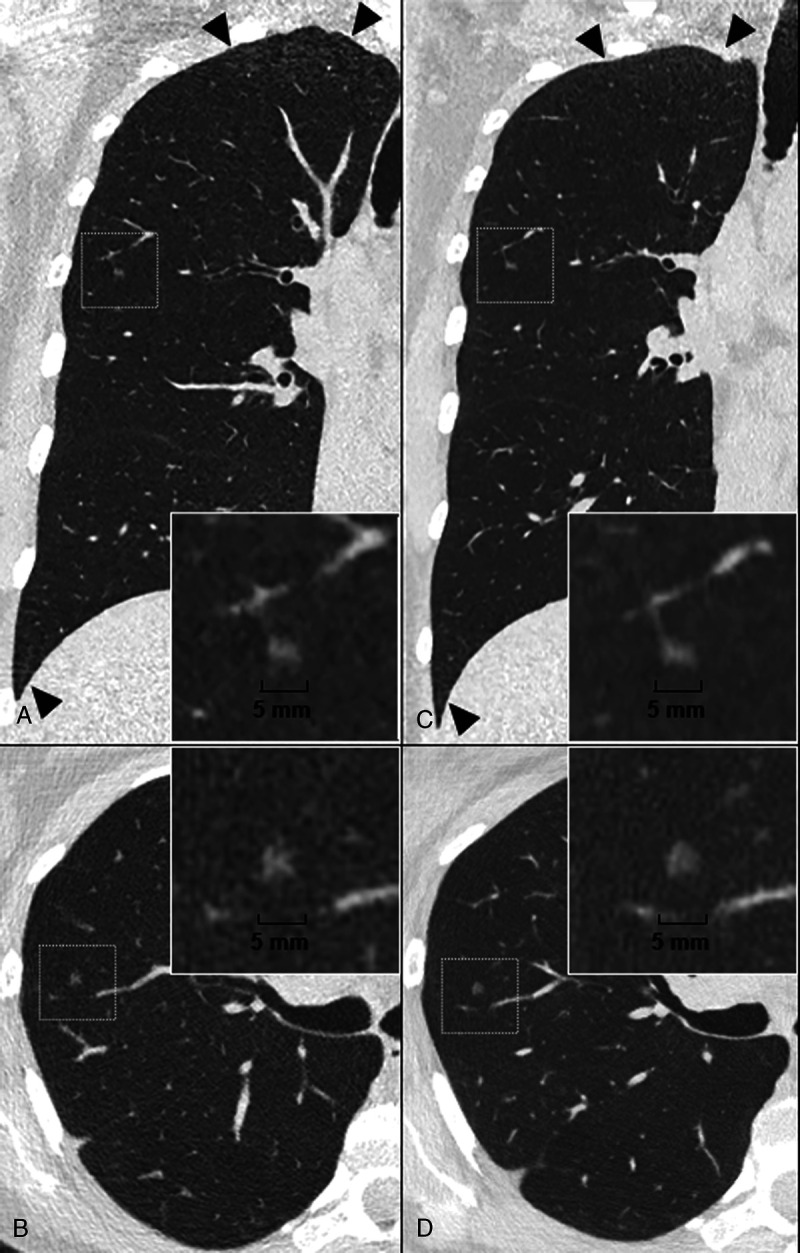
Case study of a pure ground glass nodule (GGN) on a lung low-dose ultra-high resolution (LD-UHR) imaging in a 44-year-old woman using energy-integrating dual-layer detector CT (EID-DLCT; CT7500) and SPCCT systems (Philips Healthcare) (A–B, coronal and axial EID-DLCT images; C–D, coronal and axial SPCCT images; in small boxes, zoom magnification of the GGN). Compared with EID-DLCT, SPCCT images lead to a better, comprehensive assessment of GGN, showing a round shape, a higher volume confirmed by an automatic segmentation (30.6 mm3 vs 24 mm3, ie, an 25% increase) and a link with a fine vessel from an adjacent segmental pulmonary vein/artery, possibly suggestive of adenomatous hyperplasia. SPCCT images also show the reduction in noise in the upper and lower part of the lungs (black arrowheads).
