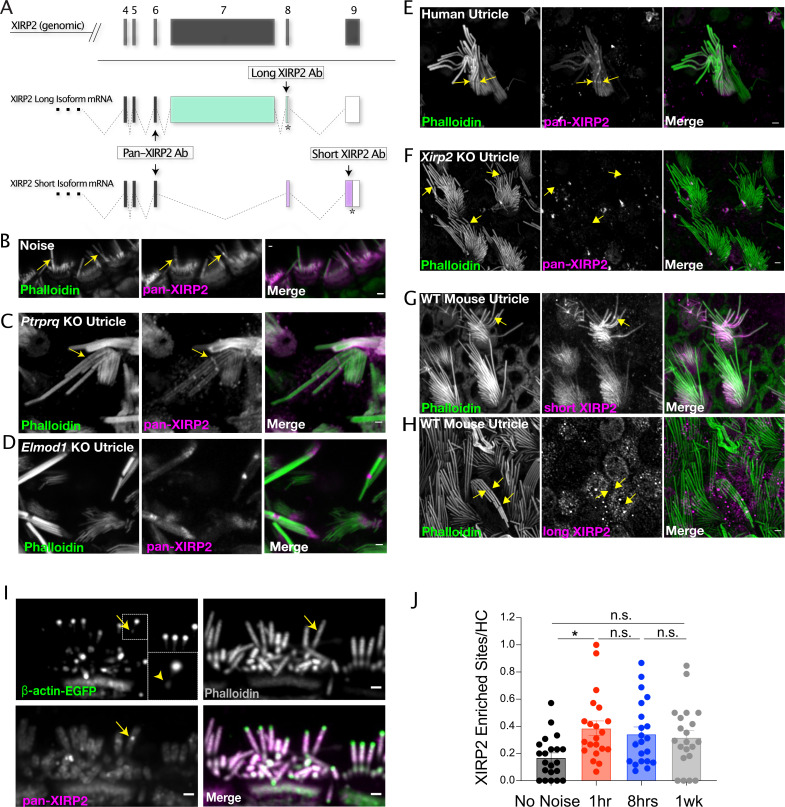
Figure 3. The short isoform of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) is enriched at gaps and remains there after repair.
(A) Diagram of Xirp2 gene structure and isoforms indicating the positions encoding the epitopes recognized by antibodies used in the figure. (B) XIRP2 enrichment at gaps (yellow arrows) in inner hair cells (IHCs) induced by overexposure to noise (120 dB broadband [1–22 kHz] for 2 hr). (C) XIRP2 enrichment at gaps in a utricle hair cell in a P25 Ptrpq knockout mouse. (D) XIRP2 enrichment in gaps (yellow arrows) in IHCs in a P20 Elmod1 knockout mouse. (E) XIRP2 enrichment at gaps (yellow arrows) in a human utricle hair cell. (F) XIRP2 staining is absent in Xirp2 knockout utricle hair cells. (G) Short XIRP2 is enriched at gaps (yellow arrows). (H) Long XIRP2 is excluded from the hair bundle and not present in gaps (yellow arrows). (I) XIRP2 enrichment is colocalized with sites of enriched synthesized β-actin synthesized after noise exposure that likely represent repaired gaps (yellow arrow). (J) The number of XIRP2 enriched sites in stereocilia increases following noise exposure (No Noise vs 1 hr, *, p=0.039, 1 hr vs 8 hr - n.s., p=0.956, 8 hr vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.979, No Noise vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.227). n=7 organs of Corti; 4 mice per group. All scale bars are 1 μm. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Images are representative of >3 experiments.