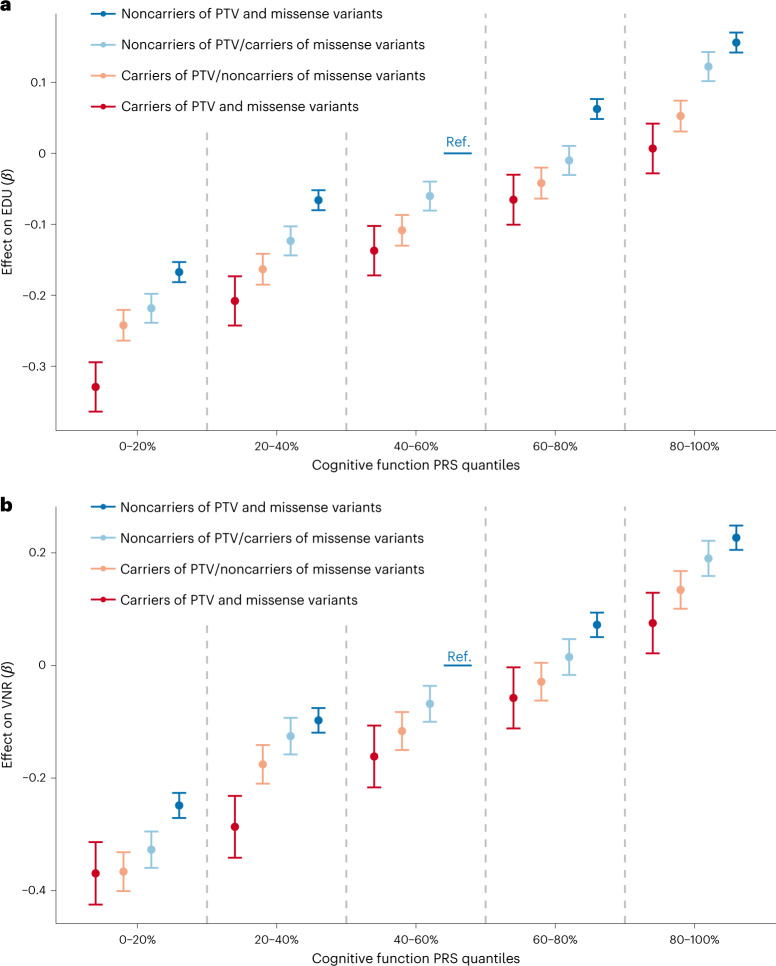
Fig. 5. Contribution of common and rare coding variants to EDU and VNR.
a,b, The impact of cognitive function PRS and carrier status of PTV or damaging missense variants (MPC > 2) in LOF-intolerant genes (pLI > 0.9) on EDU (a) and VNR (b). Unrelated UKB EUR samples were included in this analysis with n = 318,844 for EDU and n = 128,812 for VNR. EDU and VNR were residualized by sex, age, age2, sex by age, sex by age2, top 20 principal components and recruitment centers and rank-based inverse-normal transformed. The effect (and 95% CI) of PRS and rare coding variant carrier status on residualized, transformed EDU/VNR was estimated using linear regression, with noncarriers of PTV and damaging missense variants with PRS in the middle quantile as the reference (Ref.) group. Data are presented as effect size estimates (β) with 95% CIs.