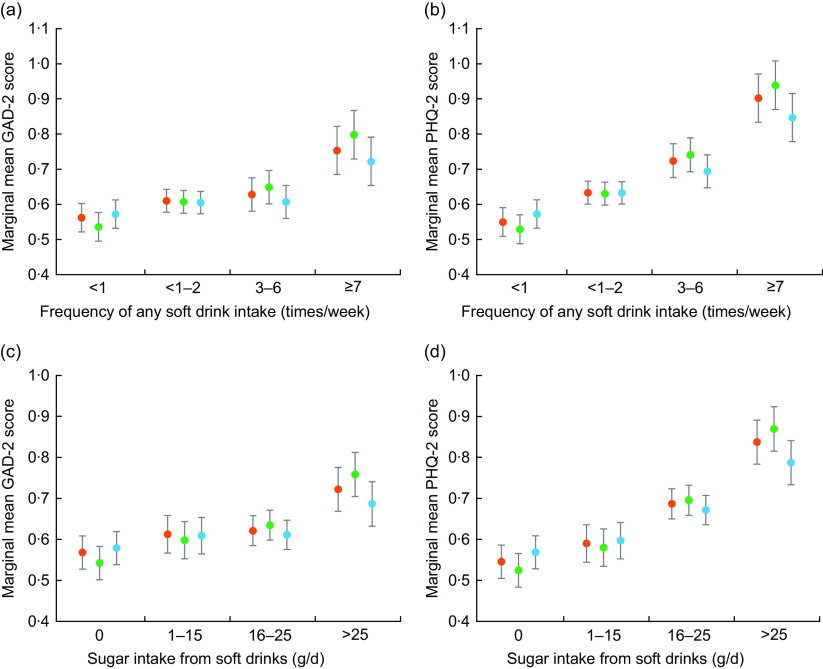
Fig. 3.
Unadjusted and adjusted mean scores of anxiety (measured using the two-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-2)) and depression (measured using the two-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-2)), grouped by frequency of any soft drink intake or quartile of sugar intake from soft drinks, in the sample of students (n 8085) newly enrolled in a comprehensive university in Changsha, China, 2017. (a) GAD-2 mean scores and frequency of any soft drink intake; (b) PHQ-2 mean scores and frequency of any soft drink intake; (c) GAD-2 mean scores and quartile of daily sugar intake from any soft drinks; (d) PHQ-2 mean sores and quartile of daily sugar intake from any soft drinks ( , means estimated from unadjusted model;
, means estimated from unadjusted model;  , means estimated from model adjusted for demographic factors;
, means estimated from model adjusted for demographic factors;  , means estimated from model adjusted for demographic and behavioural factors). Means, with their 95 % CI represented by vertical bars, were estimated from two-level linear models with students as level 1 and province as level 2. Demographic factors include age, gender, ethnicity and annual household income. Behavioural factors included daily water intake, alcohol drinking, passive smoking, sport, sedentary activities, defecation and BMI
, means estimated from model adjusted for demographic and behavioural factors). Means, with their 95 % CI represented by vertical bars, were estimated from two-level linear models with students as level 1 and province as level 2. Demographic factors include age, gender, ethnicity and annual household income. Behavioural factors included daily water intake, alcohol drinking, passive smoking, sport, sedentary activities, defecation and BMI