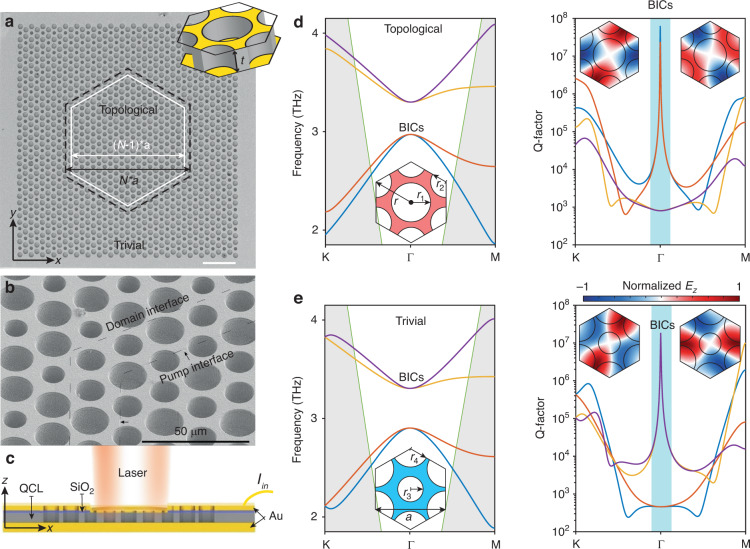
Fig. 1. Fabricated sample and bound state in the continuum (BIC) features of the quadrupolar band edges.
a, b The scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the fabricated laser cavity, where the pump region with lateral periodic number of N-1 is the topological nontrivial domain encircled by the dashed white hexagon box. The actual interface between the trivial and nontrivial domains is indicated by the black box, where the topological bulk cavity has lateral periodic number of N. The scale bar in (a) indicates 100 μm. The inset show the 3D perspective view of the designed photonic supercell with QCL thickness of 13 μm. c The cut-view (schematic) of the laser device. d, e Band structures and Q-factors of the topological and nontrivial supercells under periodic boundary conditions. The gray shadows show the region that is below the light line. The supercell structures for the trivial and nontrivial domains are shown by the insets, respectively. The lattice constant μm, and the radius of the hexagon . With fabrication error taken into consideration (see Supplementary Materials for details), the topological and trivial supercells have geometric parameters of , , and , respectively. The quadrupolar modes ( and with the normalized electric fields, z-components, shown by the inset mode profiles) show BIC features as their Q-factors tend to diverge to infinity at the Brillouin zone center (Γ point). The cyan belts show the regions where the quadrupolar modes appear as BICs and they have inversed frequencies for the topological case