Table 7.
Family aggregation of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in eight Mesoamerican countries, 2011–2013
| Mothers, fathers, and children | Mothers and fathers | Mothers and children | Fathers and children | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation, r * (95 % CI) | – | 0·23 | 0·10, 0·35 | 0·49 | 0·38, 0·58 | 0·24 | 0·11, 0·36 | |
| Intraclass correlation† | ||||||||
| Within-family variance | 282·8 | 345·0 | 215·7 | 285·3 | ||||
| Between-family variance | 127·1 | 101·7 | 191·6 | 87·6 | ||||
| ICC‡ (95 % CI) | 0·31 | 0·23, 0·40 | 0·23 | 0·13, 0·37 | 0·47 | 0·37, 0·57 | 0·23 | 0·13, 0·38 |
Pearson correlation coefficient.
Variance partitioned from a linear random-effects model with serum 25(OH)D as the continuous outcome and a random effect for family. Separate models were fitted to partition the variance for each combination of two family members.
Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC)=
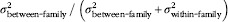 . 95 % CI were calculated using the delta method(
17
).
. 95 % CI were calculated using the delta method(
17
).
