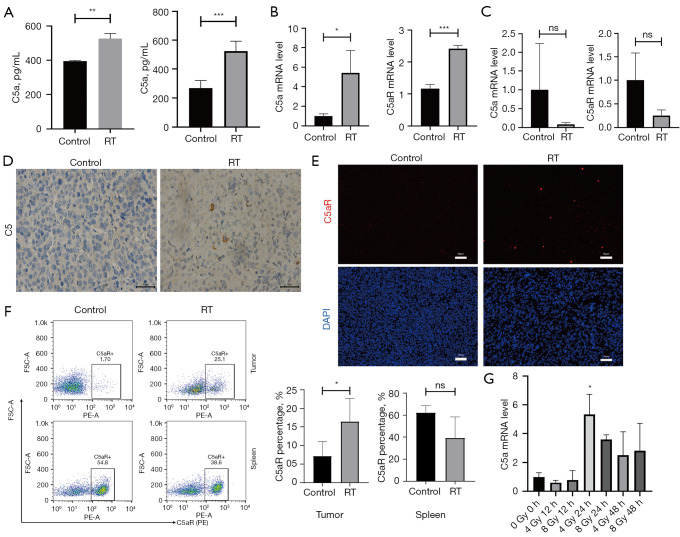
Figure 4.
RT promotes the release of C5a on tumor cells and leads to up-regulation of C5aR expression. (A) C5a concentration in blood and tumor tissue homogenates measured by ELISA. qRT-PCR analysis of the mRNA levels of C5a and C5aR in tumor (B) and spleen tissues (C). (D) Representative images of C5 staining in tumor tissues in irradiated and untreated groups. IHC staining; scale bars represent 40 µm. (E) IF of tumors in irradiated and untreated groups. Sections were stained with an antibody recognizing C5aR (red) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars represent 50 µm. Representative images are shown. (F) Flow cytometry assays were performed to indicate that C5aR were significantly upregulated in tumor tissues not in spleen tissues of irradiated mice. (G) Relative mRNA levels of C5a were calculated in tumor cells at different time points after different dose of RT. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ns, not significant. RT, radiotherapy; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; FSC-A, forward scatter-A; PE-A, phycoerythrin-A; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; mRNA, messenger RNA; IF, immunofluorescence; IHC, immunohistochemistry.