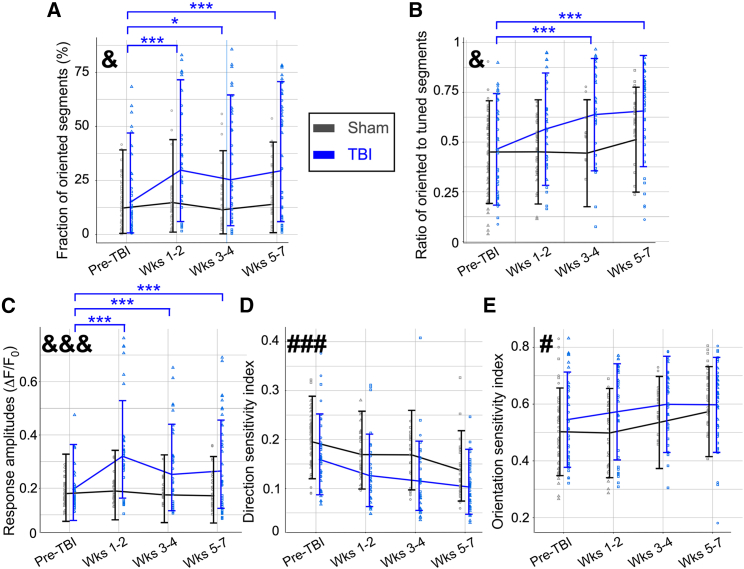
Figure 2.
Multimodal TBI causes long-term deficits to thalamocortical axonal activity patterns and tuning to visual stimulation
(A) The fraction of oriented segments showed a significant group-by-time interaction (p = 0.015, F-test) with a significant increase in the fraction of oriented segments observed in all post-TBI over pre-TBI for the TBI group (Holm-adjusted p < 0.05 in post-hoc comparisons of time within experimental group) but not for the sham control group (Holm-adjusted p > 0.05 for all paired time comparisons). &, p < 0.05 for group-by-time interaction; ∗, p < 0.05 for TBI within-group time differences; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001 for TBI within-group time differences.
(B) The ratio of oriented-to-tuned segments showed a significant group-by-time interaction (p = 0.015, F-test) with a significant increase in the measured ratio for the TBI group after TBI (Holm-adjusted p < 0.001 and p < 0.0001 for pre-TBI vs. weeks 3–4 and 5–7, respectively) but no significant changes for the sham control group (Holm-adjusted p > 0.05 for all time comparisons).
(C) The measured fluorescence response amplitudes for a drifting grating simulation showed a group-by-time interaction (p < 0.0001, F-test), and model-estimated mean amplitudes were 63% higher in TBI mice in the first 1–2 weeks after TBI compared with the pre-TBI period (Holm-adjusted p < 0.0001). Response amplitudes remained higher by 29% and 35% on weeks 3–4 and 5–7, respectively (Holm-adjusted p < 0.01 and p < 0.001 respectively). The sham control group did not show such an increase, and there was no significant difference in time effects between them (Holm-adjusted p > 0.05 for all time comparisons).
(D) The median DSI value of the tuned segments showed a significant decrease over time for both groups (p < 0.0001, F-test) but without a group-by-time interaction (p = 0.541, F-test). ###, p < 0.001 for time effect.
(E) The median OSI value of the tuned segments showed a significant increase over time for both groups (p = 0.029, F-test) but without a group-by-time interaction (p = 0.522, F-test; same FOVs as in C). Within each group, median data from individual mice are represented by different markers (square, triangle, circle). The lines connect the model-estimated marginal mean values, and the error bars show the model-estimated 95% confidence intervals. Figures and models each include 268 measures of 41 FOVs in 6 mice (3 per experimental group).