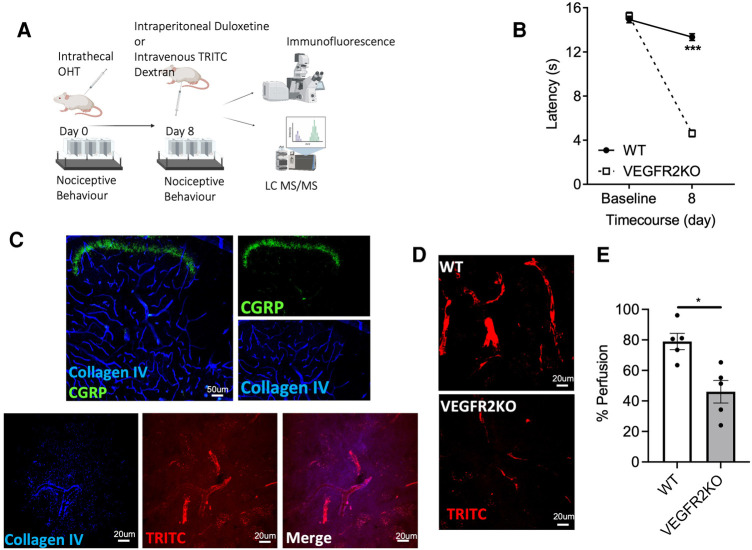
Figure 1.
A transgenic rodent model of vasculopathy. (A) Experimental timeline is outlined in the diagrammatic figure. Both VEGFR2KO (Tie2CreERT2 positive x vegfr2fl/fl) mice and WT (Tie2CreERT2 negative x vegfr2fl/fl) mice were administered with hydroxytamoxifen (1 µM) via intrathecal injection. (B) 8 days post hydroxytamoxifen injection, a pronounced heat hypersensitivity in VEGFR2KO mice developed. This was demonstrated through a decrease in withdrawal latency when compared to WT mice (***P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA with post-Sidak multiple comparison test, N = 8 WT, N = 10 VEGFR2KO; WT mean ± SEM: 13.14 ± 0.37 s vs. VEGFR2KO mean ± SEM: 4.61 ± 0.30 s). (C) Representative images of capillary network in the mouse lumbar dorsal horn. (C, upper panel) Collagen IV (basement membrane marker) and superficial dorsal horn marker (CGRP) demonstrates the extensive vascular network throughout the dorsal horn. (C, Lower Panel) TRITC (Red) perfused lumbar spinal cord cryosections stained with basement membrane marker (collagen IV; Blue). (D) There is diminished capillary perfusion in VEGFR2KO mice vs. controls, presented as a reduction in the percentage of (E) TRITC dextran perfused vessels in VEGFR2KO mice vs. controls (*P < 0.05, Paired T test, N = 5 WT, N = 5 VEGFR2KO).