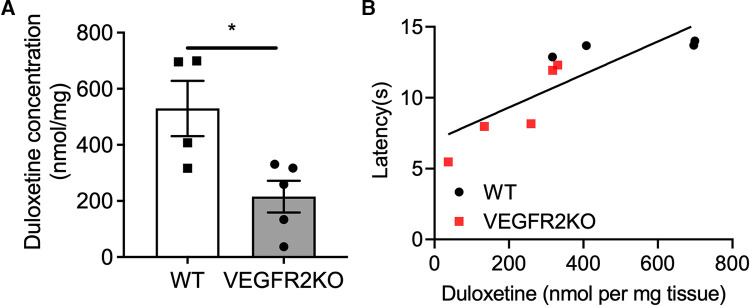
Figure 3.
Duloxetine accumulation in the spinal cord is diminished in VEGFR2KO mice and impairs analgesia. 8 days following hydroxytamoxifen treatment in WT and VEGFR2KO mice, all mice received a single intraperitoneal injection of duloxetine (20 mg/kg). (A) The lumbar region of the spinal cord was excised and abundance of duloxetine was determined using LC-MS/MS. There was a decrease in duloxetine concentration in the spinal cord of VEGFR2KO mice when compared to WT mice [*P < 0.05, Mann–Whitney Test, N = 4 WT (mean ± SEM: 519.7 ± 98.63), N = 5 VEGFR2KO (mean ± SEM: 215.7 ± 56.64)]. (B) Correlation analysis of duloxetine abundance vs. heat withdrawal latency demonstrates a strong correlation (R2 = 0.702, P < 0.01, single linear regression analysis) between duloxetine abundance and heat withdrawal latency. This demonstrates that those rodents with lowest abundance of duloxetine in the lumbar region of the spinal cord presented a lower withdrawal latency following administration (*P < 0.05, Paired T test, N = 4 WT, N = 5 VEGFR2KO).