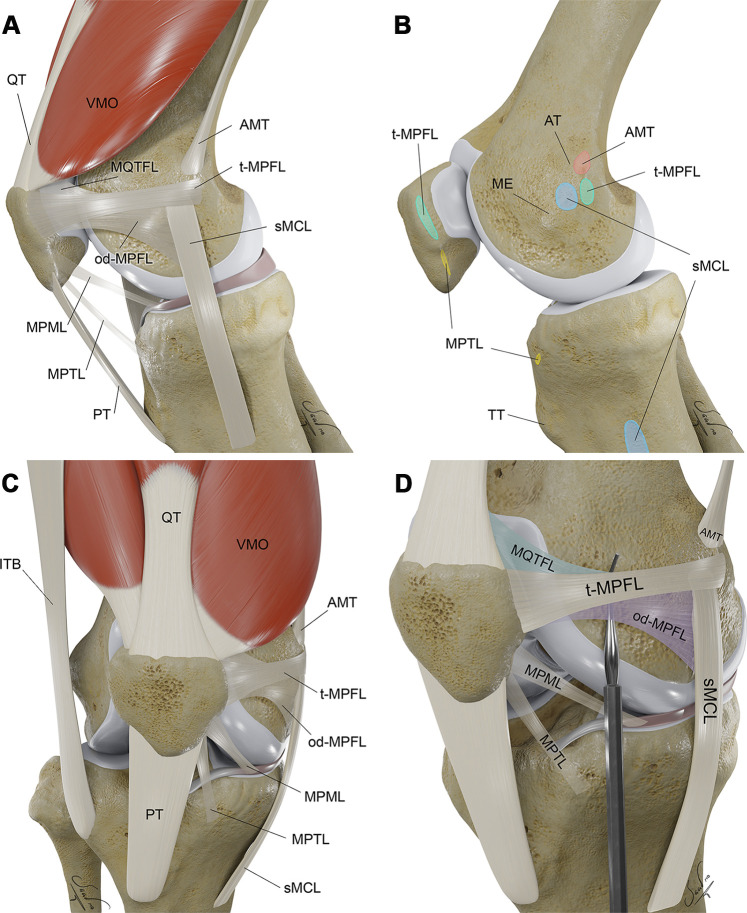
Figure 1.
Three-dimensional (3D) illustrations show key osseous and soft-tissue structures of extensor mechanism in the lateral (A, B), anterior (C), and external oblique (D) perspectives, with respective osseous attachment areas. Structures of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) complex are exaggerated by the probe (in D). AMT = adductor magnus tendon, AT = adductor tubercle, ITB = iliotibial band, ME = medial epicondyle, od-MPFL = MPFL with oblique decussation component, t-MPFL = MPFL with transverse oblique decussation component, MPML = medial patellomeniscal ligament, MPTL = medial patellotibial ligament, MQTFL = medial quadriceps tendon femoral ligament, PT = patellar tendon, QT = quadriceps tendon, sMCL = superficial medial collateral ligament, TT = tibial tubercle, VMO = vastus medialis obliquus muscle.