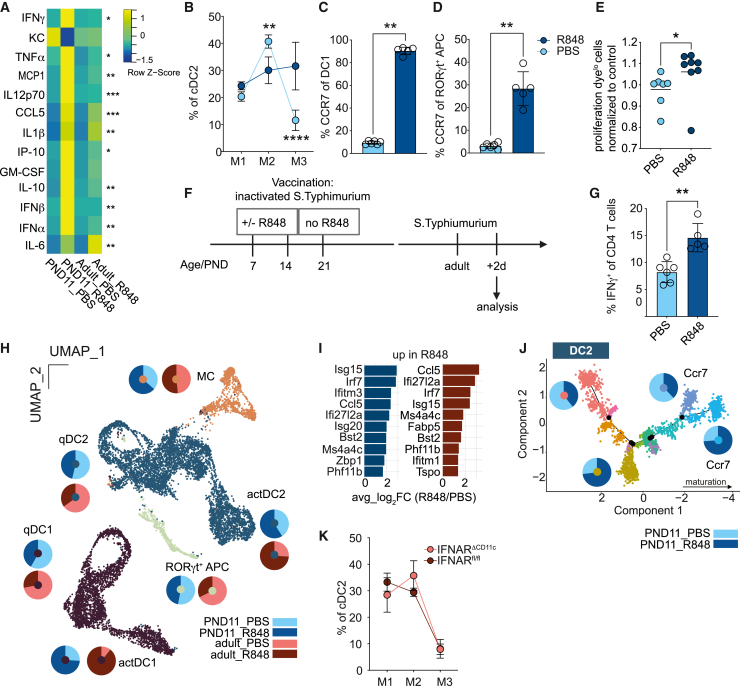
Figure 6.
IFN I induces DC activation in neonatal PP and modifies the adaptive immune response
(A) Heatmap of serum cytokines 8 h after R848 (n = 4–5; Kruskall-Wallis test, comparison within age group).
(B) Percentage of M1–M3 of cDC2 in PND11 mice after R848 (n = 4–5), (mean + SD; two-way ANOVA/Bonferroni test between treatment groups within the same maturational stage) determined by FACS.
(C and D) Percentage of CCR7+ among (C) cDC1 and (D) RORγt+ APC in PP after R848 in PND11 mice (mean + SD, Mann-Whitney U test).
(E) Proliferation dye dilution in OTII cells in PP of neonatal mice 48 h after oral gavage of OVA ± R848 normalized to mean PBS (n = 7–8, mean, Mann-Whitney U test).
(F) Neonatal PAA-STm/R848 vaccination experimental setup.
(G) Percentage of IFNγ+ of CD4+ T cells in colonic LP of STm infected mice vaccinated with PAA STm ± R848 as neonates (n = 5–6, mean + SD, Mann-Whitney U test).
(H) scRNA-seq of PP MNP (n = 1; cells pooled from 4 animals per sample).
(I) Top 10 upregulated genes in PND11 (dark blue) and adult (berry) R848 vs. PBS qDC2.
(J) Pseudotime trajectory of cDC2 from PND11 mice ± R848, pie charts represent the relative contribution of cells from PBS and R848 treated animals to indicated branches.
(K) Percentage of M1–M3 of cDC2 in adult IFNARΔCD11c and IFNARfl/fl mice (n = 5), (mean + SD, two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni test between genetic groups within the same maturational stage) determined by FACS. See also Figures S6 and S7.