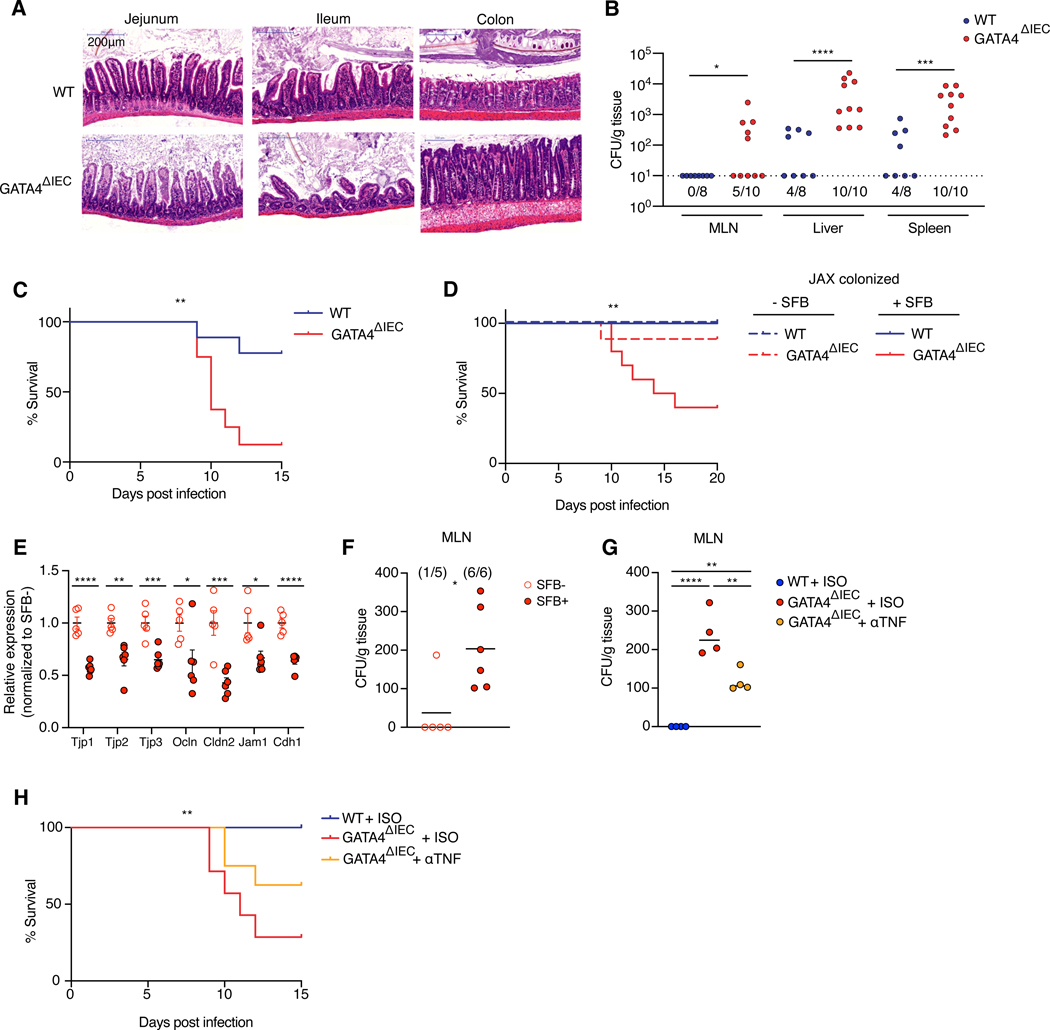
Figure 4. Dysregulated SFB colonization of the proximal intestine promotes loss of barrier function and TNF induced immunopathology upon C. rodentium infection.
(A) Representative H&E staining of each intestinal region 10 days after C. rodentium infection.
(B) CFUs of C. rodentium translocation to MLN, liver, and spleen. N= 8–10 mice/group.
(C) Percent survival of WT and GATA4ΔIEC mice 0–15 days post C. rodentium infection. N= 8–9 mice/ group.
(D) Percent survival of JAX colonized WT (blue) and GATA4ΔIEC (red) in SFB associated (solid lines) or SFB free mice (dashed lines) 0–20 days post C. rodentium infection. N= 6 WT mice/group, N= 9 GATA4ΔIEC – SFB mice/group, N= 10 GATA4ΔIEC + SFB mice/group.
(E) Relative expression as measured by qPCR of tight junction proteins to GAPDH in the jejunum of SFB free (open circles) or SFB colonized (filled circles) GATA4ΔIEC mice 5 days after infection. N= 5–6 mice/group.
(F) CFUs of C. rodentium translocation to MLN of SFB free or SFB colonized GATA4ΔIEC mice 5 days after infection. N= 5–6 mice/group.
(G) CFUs of C. rodentium translocation to MLN of SFB positive WT isotype, GATA4ΔIEC isotype, or GATA4ΔIEC αTNF treated mice 5 days after infection. N= 4 mice/group.
(H) Percent survival of WT isotype treated, and GATA4ΔIEC isotype treated, or αTNFα treated mice 0–15 days post C. rodentium infection. N= 7–9 mice/ group.
All data in this figure are pooled from at least two-independent experiments and represented as mean or mean± SEM. **** P<0.0001 , *** P<0.001, ** P<0.01, * P<0.05, Mann-Whitney test (B), Mantel-Cox test (C, D, H), t-test (E), Mann-Whitney test (F), ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison test (G).