Figure 2.
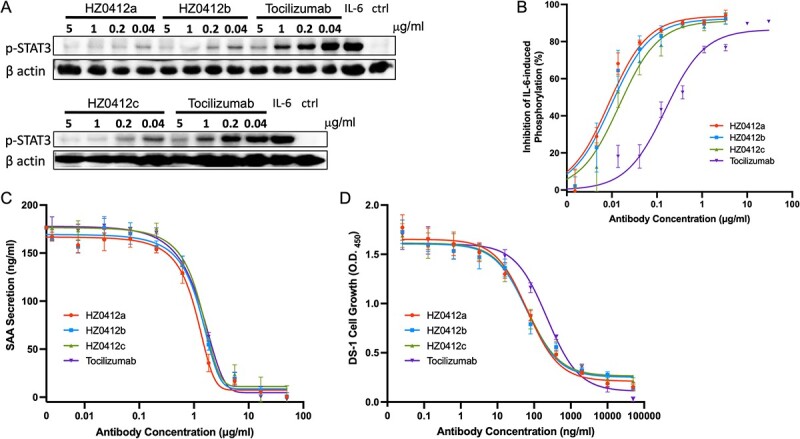
IL-6 signaling is blocked by HZ0412a and its variants in vitro. (A) All humanized IL-6R antibodies inhibited IL-6-induced phosphorylation of STAT3 in DLD-1 cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Cells were stimulated with rhIL-6 and the phosphorylation of STAT3 at Tyr705 was detected by a phosphorylation site–specific antibody as described in section Materials and Methods. A representative western blot result is shown. β actin was chosen to monitor equal loading of samples. (B) Summary of phosphorylation inhibition experiments. The specific phosphorylation signals on western blot were quantified and normalized with corresponding β actin signals. The normalized signals in the absence of IL-6R antibodies are used as a reference (100%), and the degrees of signal reduction are plotted against the concentrations of antibodies. (C) The inhibition of IL-6/IL-1β-induced SAA secretion by IL-6R antibodies in Hep G2 cells is concentration-dependent. Hep G2 cells (2 × 105) were stimulated with IL-6 and IL-1β with or without antibodies as described in section Materials and Methods. The supernatant was collected for the measurement of SAA by ELISA. (D) IL-6-induced DS-1 cell growth can be suppressed by IL-6R antibodies in a concentration-dependent manner. To quantify the DS-1 cell proliferation, the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) was used, and the results are expressed as mean absorbance at 450 nm with SD values. Tocilizumab was included as a positive control. All experiments were repeated at least three times.
