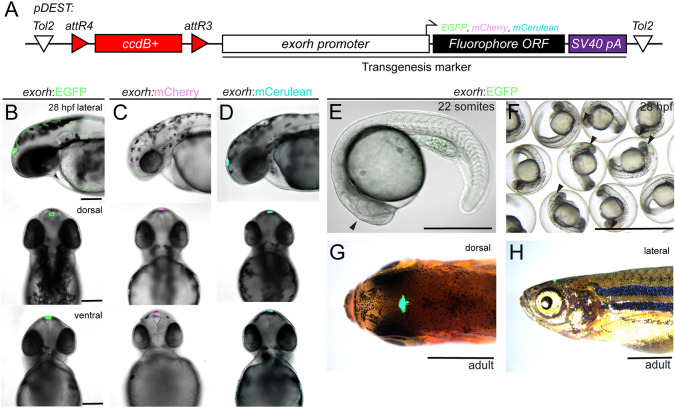
Fig. 5.
Labeling the zebrafish pineal gland with the exorhodopsin (exorh) regulatory region as a transgenesis marker. (A) Schematic of the Tol2 secondary transgenic marker backbones pCK017 pDEST-exorh:EGFP, pCK053 pDEST-exorh:mCherry and pCK054 pDEST-exorh:mCerulean, including the attR4- and attR3-flanked ccdB cassette followed by the1055 bp exorh promoter driving EGFP, mCherry or mCerulean. (B-D) Stable transgenic lines for EGFP-, mCherry- and mCerulean-based exorh-driven fluorophore reporters; lateral, dorsal and ventral views at 2 dpf showing specific, easily detectable reporter activity in the pineal gland. (E-H) Stages and appearances of exorh-driven transgenesis reporters. Starting at the 22-somite stage (E), exorh:EGFP expression (black arrowhead) is easily detectable in individual embryos and in groups under a standard dissecting microscope (F), while embryos are still in their chorions. exorh-driven fluorophore expression persists into adulthood, as seen in dorsal (G) and lateral (H) views; dissecting microscope images. Scale bars: 200 μm (B-D); 500 μm (E); 0.25 cm (F); 0.5 cm (G,H).