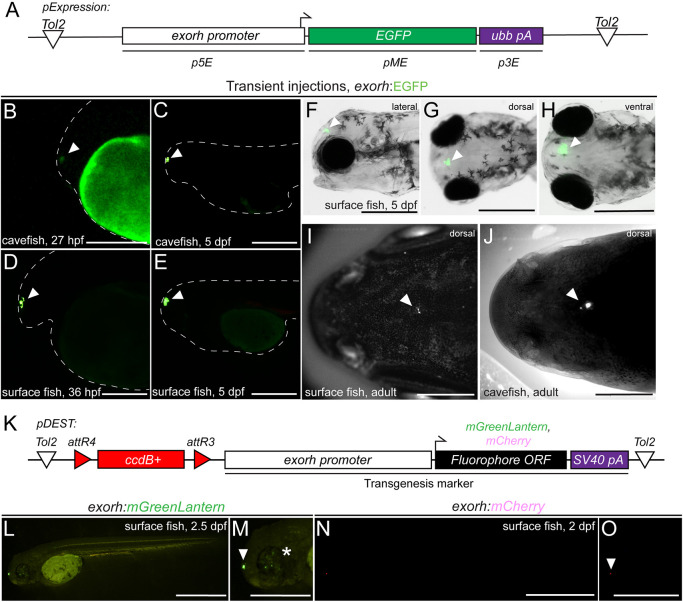
Fig. 7.
The exorh-based transgenesis marker functions in Mexican cavefish (Astyanax mexicanus). (A) Tol2 expression vector using the zebrafish exorh promoter driving the expression of EGFP; see also Fig. 5. (B-E) Transient injection of exorh:EGFP shows reporter activity in the pineal gland of both Tinaja cavefish at 27 hpf (B) and 5 dpf (C), as well as in surface fish at 36 hpf (D) and 5 dpf (E). Pineal expression is indicated with an arrowhead and embryo morphology traced with a dashed line. (F-H) Lateral, dorsal and ventral views at 5 dpf showing specific, easily detectable EGFP reporter activity in the pineal gland (arrowheads). (I,J) Grayscale images of live exorh:EGFP-injected animals, detection of EGFP (white dots) in surface and cavefish adults (arrowheads). (K) Schematic of Tol2-based transgenesis backbones pDEST-exorh:mGreenLantern and pDEST-exorh:mCherry, including the attR4 and attR3-flanked ccdB cassette, and the 1055 bp zebrafish exorh promoter driving mGreenLantern or mCherry for Multisite Gateway cloning. (L,M) Injection of the exorh:mGreenLantern-containing Tol2 Destination vector shows pineal gland expression (arrowhead) as well as patchy retinal expression in developing surface fish (asterisk). (N,O) Injection of the exorh:mCherry-expressing Tol2 destination vector, showing pineal gland expression in developing cavefish (arrowhead). Scale bars: 200 μm (B-E,M,O); 500 μm (F-H,L,N); 1 cm (I,J).