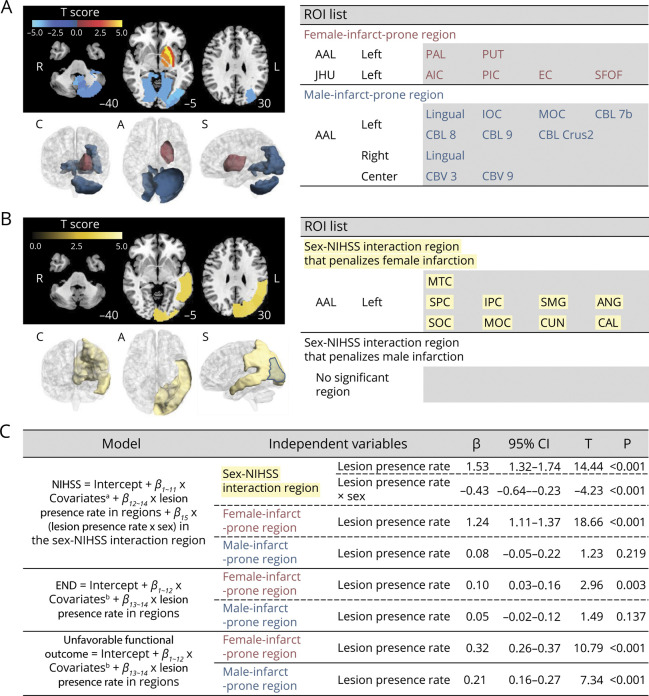
Figure 4. Multivariable Brain Mapping and Regression Analyses to Investigate Sex-Dependent Associations of the Lesion Presence Rates in Sex-Related Brain Regions With Admission NIHSS Score, the Incidence of END, or the Incidence of Unfavorable Functional Outcome.
(A) Female infarct-prone and male infarct-prone ROIs (anatomic ROIs different between sexes) showing a significant sex difference in the regional lesion probability. Top left. ROI-wise t scores for the sex difference in the lesion probabilities are displayed with color coding (red/orange for female patients and blue shades for male patients) on the axial images of Montreal Neurological Institute brain templates (z-axis coordinates = −40, −5, and 30). L and R denote left and right, respectively. Bottom left. A 3-dimensional representation of the significant ROIs is displayed. C, A, and S denote coronal, axial, and sagittal views, respectively. Right. A complete list of the significant ROIs, with their labels from the AAL and JHU atlases. (B) Sex-NIHSS interaction ROIs showing similar anatomic areas with different sex-related impact on admission NIHSS score, suggesting intrinsic (as opposed to anatomic) sex differences. Unlike these intrinsic ROIs that penalize female infarction, there is no ROI that penalizes male infarction. An intrinsic ROI (left middle occipital cortex) that overlaps with the male infarct-prone anatomic ROIs is outlined in blue. Note that there was no significant sex-END incidence interaction region or sex unfavorable outcome interaction region (eFigures 6 and 7, links.lww.com/WNL/C780). (C) Multivariable regression analyses to show sex-related associations of the lesion presence rate (=number of infarct-positive ROIs/number of all ROIs) in each of the sex-related brain regions (female infarct-prone and male infarct-prone regions with or without sex-NIHSS interaction region) with the NIHSS score, the incidence of END, or the incidence of unfavorable functional outcome (3-month modified Rankin Scale score >2). βs indicate β coefficients, and Ts indicates t statistics for independent variables in the regression models. AIC = anterior limb of internal capsule; AAL = Automated Anatomical Labeling; ANG = angular gyrus; CAL = calcarine; CBL = cerebellum; CBV = cerebellar vermis; CUN = cuneus; EC = external capsule; END = early neurologic deterioration; IOC = inferior occipital cortex; IPC = inferior parietal cortex; JHU = Johns Hopkins University; MOC = middle occipital cortex; MTC = middle temporal cortex; NIHSS = NIH Stroke Scale; PAL = pallidum; PIC = posterior limb of internal capsule; PUT = putamen; ROI = region of interest; SFOF = superior fronto-occipital fasciculus; SMG = supramarginal gyrus; SOC = superior occipital cortex; SPC = superior parietal cortex.